Fig. 5.
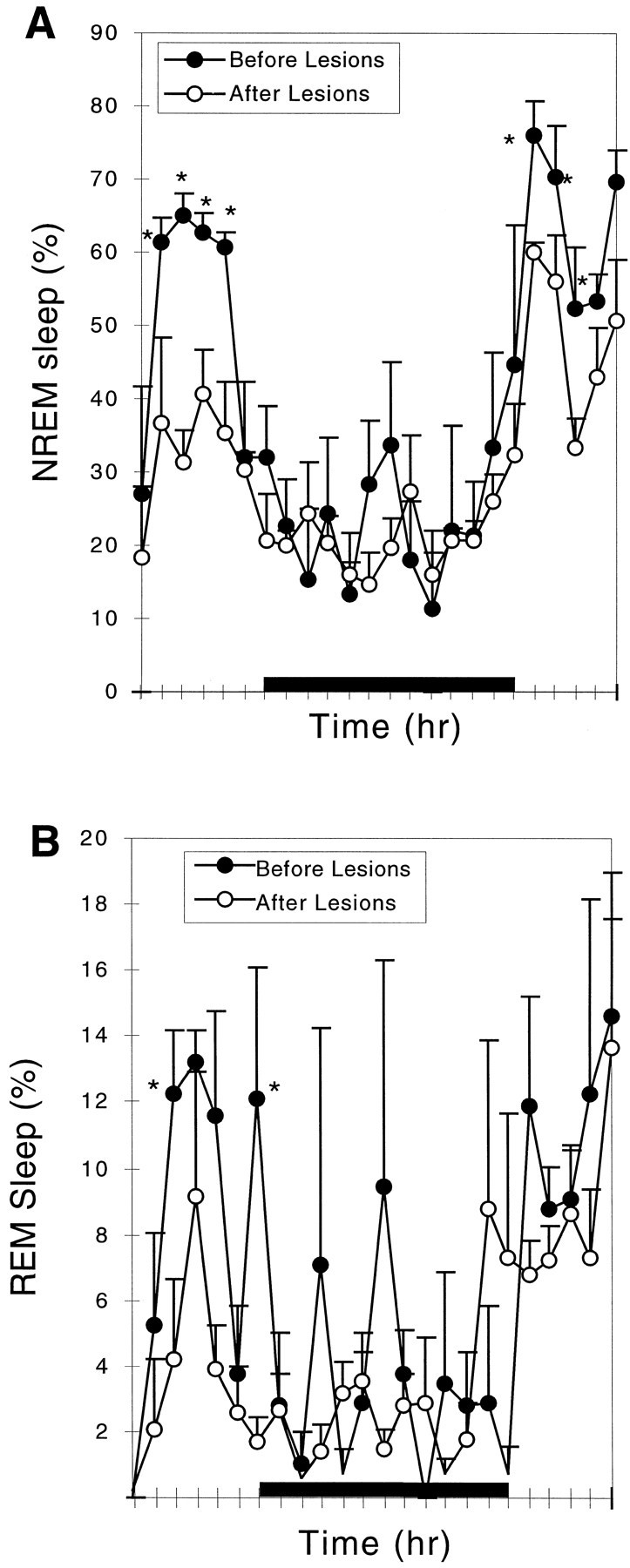
Comparison of NREM and REM sleep before and after lesion of the medial preoptic area. The lesion caused a reduction in NREM sleep by 24.5% (A) and in REM sleep by 30% (not statistically significant; B). Loss of NREM sleep was predominantly late in the light cycle, whereas the reduction of REM sleep also involved loss of peaks during the dark cycle. *p < 0.05.
