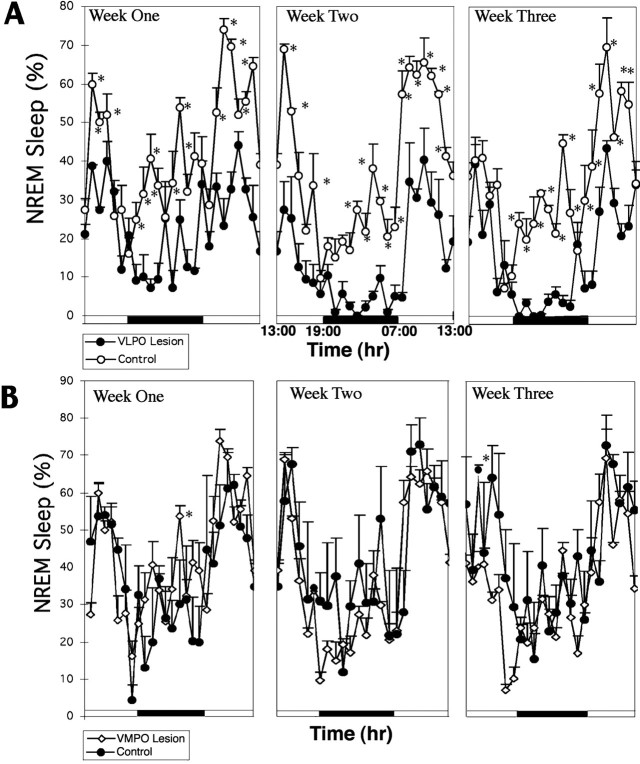
Fig. 7.
Change in NREM sleep time over a 3 week period after lesions of the VLPO (A) andVMPO (B). A, In four animals with 70–90% bilateral lesions of the VLPO cluster, the percentage of NREM sleep time was depressed by almost 45% in the first week, 63% in the second week, and 57% in the third week compared with that of a group of control rats that had received bilateral saline injections. As in the short-term experiments, the animals with VLPO lesions showed almost complete loss of NREM sleep during the dark cycle and substantial loss at the onset of the light cycle (*p < 0.05). There was no trend toward recovery. B, In five animals with severe bilateral lesions of the ventromedial preoptic nucleus, there was no change in NREM sleep time compared with that of saline-injected control animals.