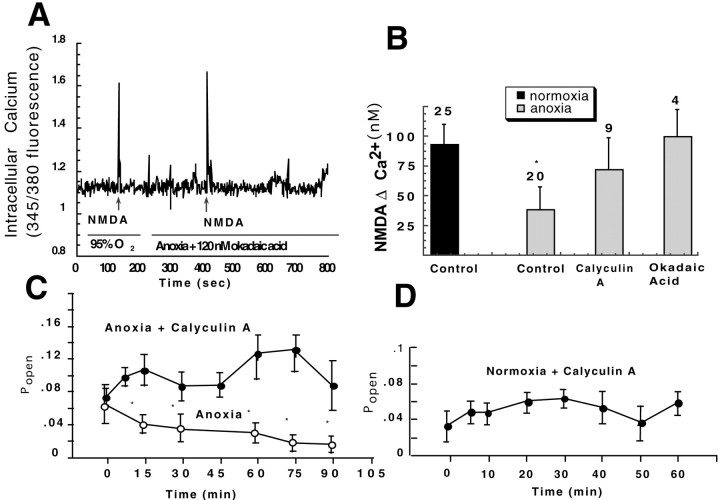
Fig. 4.
Role of phosphatases in the regulation of NMDA receptors during anoxia. A, Example showing that the nonspecific phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid prevents NMDA receptor inactivation in a dissociated pyramidal neuron during anoxia.B, Phosphatase inhibitors prevent receptor silencing in cortical sheets during anoxia. Bars show mean NMDA Δ Ca2+ responses during normoxia, anoxia, and anoxia with 1 μm calyculin or 120 nm okadaic acid.Numbers above bars indicate n values. *p < 0.05 compared with oxic control (Dunnett's test). C, Decreases in NMDA receptor open probability during anoxia are prevented with calyculin A (1 μm). *p < 0.05 denotes significant difference from control (Dunnett's test); n = 9, both groups.D, Calyculin does not affect NMDA receptor open probability with oxygen available; n = 5.