Fig. 6.
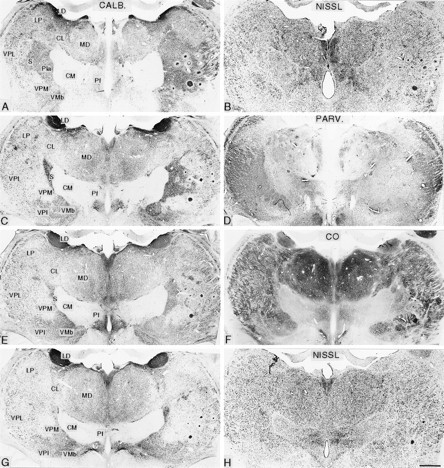
Pairs of symmetrically cut frontal sections of the diencephalon in posterior (A, B) to anterior (G, H) order from an animal that survived for 21.2 years after rhizotomy. The left member of each pair is stained immunocytochemically for calbindin (CALB; A, C, E, G), and the other is stained either by the Nissl method (B, H), immunocytochemically for parvalbumin (PARV.; D), or for cytochrome oxidase (CO; F). These show the ventral posterior nuclear complex of the thalamus ipsilateral (left) and contralateral (right) to the rhizotomies. On the affected (right) side, there is foreshortening of the VPL nucleus and loss of the posterodorsal part of the arcuate lamella that normally separates the VPM nucleus from VPL. There is expansion of the calbindin-rich S region into the area formerly occupied by the affected part of the ventral posterior complex. CL, Central lateral nucleus; CM, centre médian nucleus; LD, lateral dorsal nucleus;LP, lateral posterior nucleus; MD, mediodorsal nucleus; Pf, parafascicular nucleus; Pla, anterior pulvinar nucleus; VMb, basal ventral medial nucleus; VPI, ventral posterior inferior nucleus.Circular profiles in right thalamus are microelectrode tracks. Scale bar, 1 mm.
