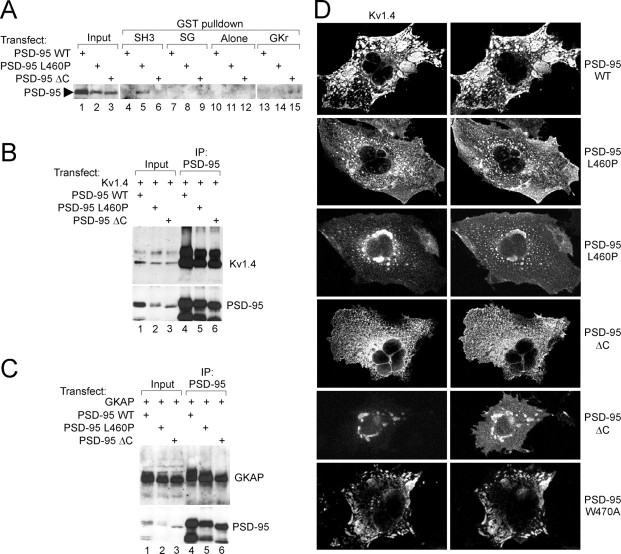
Fig. 3.
PSD-95 mutants defective in intramolecular SH3–GK interaction still bind to Kv1.4 and GKAP, but cannot cluster Kv1.4.A, GST pull-down assay confirming dominance of the intramolecular SH3–GK interaction in mammalian cells. Wild-type and mutant (L460P and ΔC) PSD-95 proteins expressed in COS cells were incubated with GST-fusion proteins of the PSD-95 SH3 domain, GK region, or combined SH3–GK (SG) regions, or with GST alone. Precipitates were immunoblotted with PSD-95 antibody. Input, 10% of COS cell extract used in pull-down assay. B, Coimmunoprecipitation of Kv1.4 with wild-type and mutant PSD-95 proteins. COS cells doubly transfected with Kv1.4 and wild-type or mutant (L460P and ΔC) PSD-95 were immunoprecipitated with PSD-95 antibody, and the precipitates immunoblotted for Kv1.4 and PSD-95. Input, 5% of the extract used in the immunoprecipitation. C, Coimmunoprecipitation of GKAP with wild-type and mutant PSD-95 proteins. COS cells were doubly transfected with GKAP and wild-type and mutant PSD-95, and immunoprecipitated with PSD-95 antibody, as in B, but the precipitates were immunoblotted for GKAP and PSD-95.D, Kv1.4 clustering by wild-type and mutant PSD-95 proteins. COS cells were doubly transfected with Kv1.4 and wild-type and mutant forms of PSD-95, as indicated. Distribution of Kv1.4 and PSD-95 was examined by double label immunofluorescence with Kv1.4 (left) and PSD-95 antibodies (right). Typical plaque-like coclusters formed between Kv1.4 and wild-type PSD-95 (top panels), but were not seen with PSD-95 mutants L460P and ΔC (middle panels). Instead, Kv1.4 and PSD-95 mutants were mainly diffuse; colocalization of these proteins occurred only in fine scattered puncta or in large perinucelar clusters. PSD-95(W470A) mutant, however, formed wild-type-looking clusters with Kv1.4 (bottom panels).