Fig. 1.
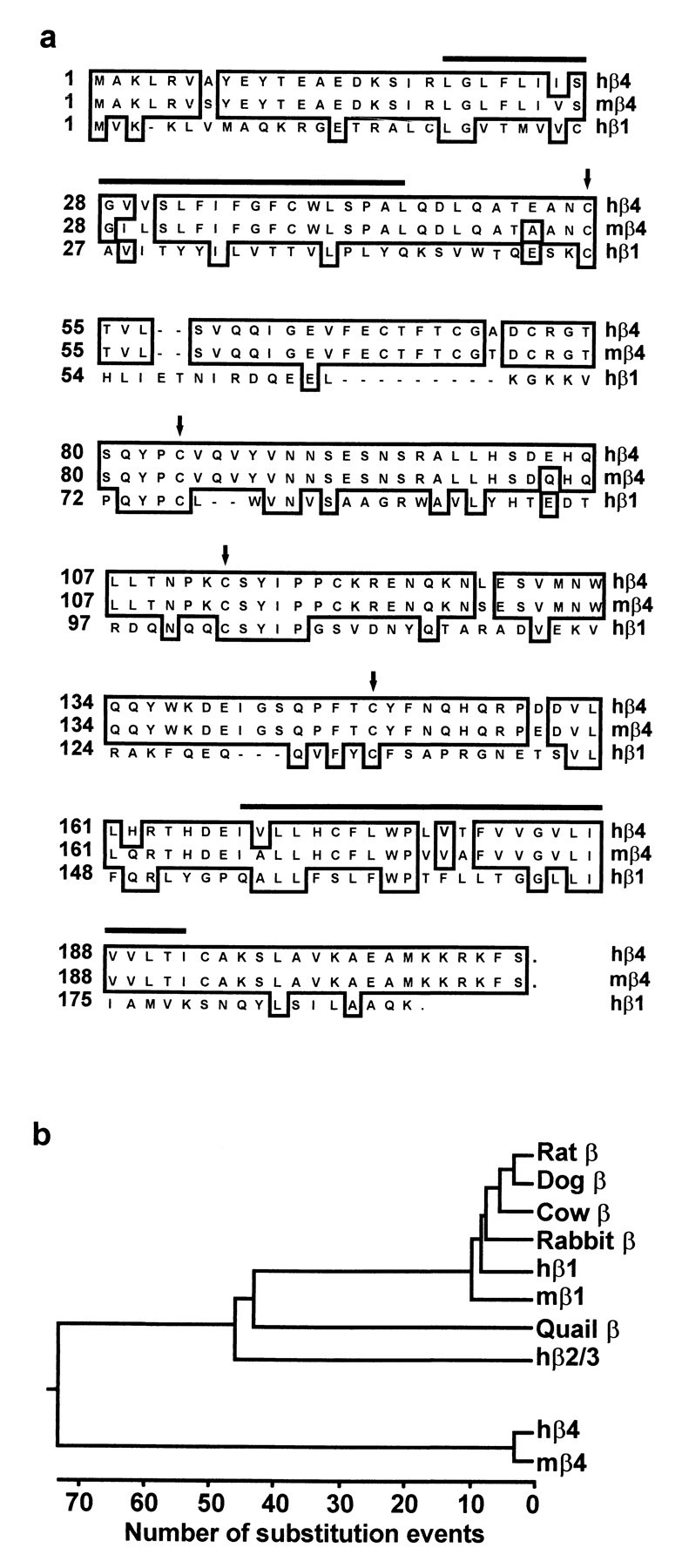
Sequence analysis of Slowpoke β subunits.a, Amino acid sequences of hβ4 (GenBank accession number AF215891), mβ4 (GenBank accession number AF215892), and hβ1 (GenBank accession number U38907) are aligned by the clustal method. Amino acids conserved in the β subunits are boxed. Thehorizontal bars indicate the two predicted membrane-spanning regions in β4, and conserved cysteine residues in the predicted extracellular loops are marked by arrows.b, Phylogenetic tree of Slowpoke β subunits cloned to date. The length of each pair of branches represents the evolutionary distance between sequence pairs, as measured by the number of substitution events. The Slowpoke β4 subunits described in this paper form a gene family distinct from other β subunits, which fall into a separate and evolutionarily conserved family. The GenBank accession numbers for the previously cloned β subunits used in this analysis are as follows: rat β, 1718491; dog β, 1127826; cow β, 508846; rabbit β, 2662318; hβ1, U38907; mβ1, 2347044; quail β, U67865; and hβ2/3, AF099137.
