Fig. 6.
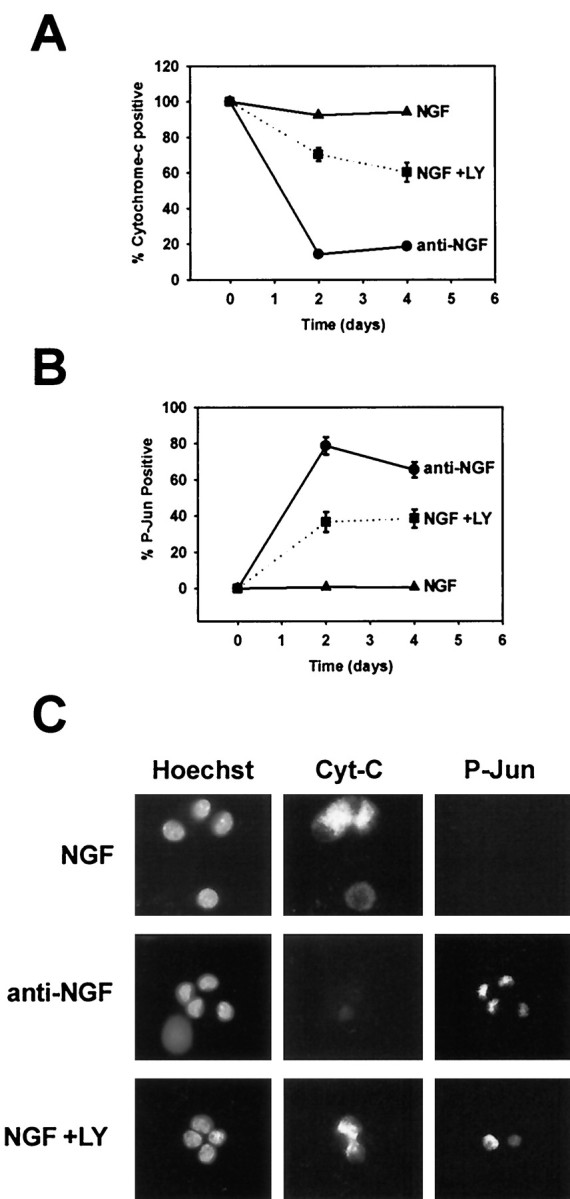
PI-3-K inhibition does not induce cytochromec release from most NGF-dependent sympathetic neurons. Sympathetic neurons were maintained in NGF (50 ng/ml), maintained in NGF with LY294002 (50 μm), or deprived of NGF for 2–4 d. The cultures were then fixed and subjected to simultaneous P-Jun and cytochrome c immunocytochemistry. Hoechst staining was also performed to identify nuclei. All conditions included BAF (50 μm) to prevent the loss of neurons. The number of cytochrome c-positive neurons (A) and the number of P-Jun-positive neurons (B) were scored in each condition and graphed as a percentage of total neurons. Note that initially more neurons are P-Jun positive a few hours after LY treatment (Fig. 1) but plateau to a lower level after 2−4 d of LY294002 treatment in the presence of BAF. C, Representative examples of immunofluorescent detection of cytochromec (Cyt-C, Alexa 488, middle column), P-Jun (Cy-3, right column), and nuclei (Hoechst, left column) in sympathetic neurons after 2 d of treatments as described above, which are listed to the left of each panel depicting each condition.
