Fig. 2.
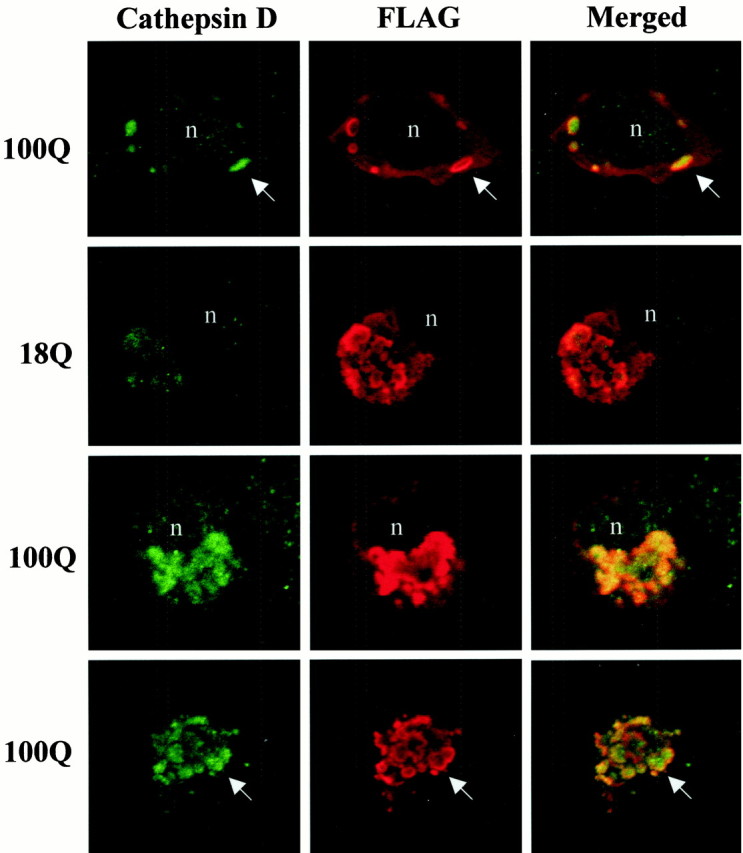
FLAG-huntingtin-immunoreactive vacuoles contain cathepsin D, and accumulation of cathepsin D is polyglutamine length-dependent. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of cells transfected with FH3221-18 or FH3221-100 then double immunostained after 24 hr for cathepsin D (green) and FLAG (red). Top three rows show intact cells, and bottom row shows a cell fragment. Dispersed vacuoles are in the cell in top row. Condensed vacuoles appear in the cells in the two middle rows. Note that FLAG-huntingtin immunoreactivity is present mainly along the periphery of the vacuole, and cathepsin D is inside the vacuole (arrows). The intensity of cathepsin D labeling in FLAG-immunoreactive vacuoles increases with polyglutamine expansion (compare two middle rows). Merged images onright show cathepsin D in green, FLAG inred, and the overlap in yellow.n, Nucleus.
