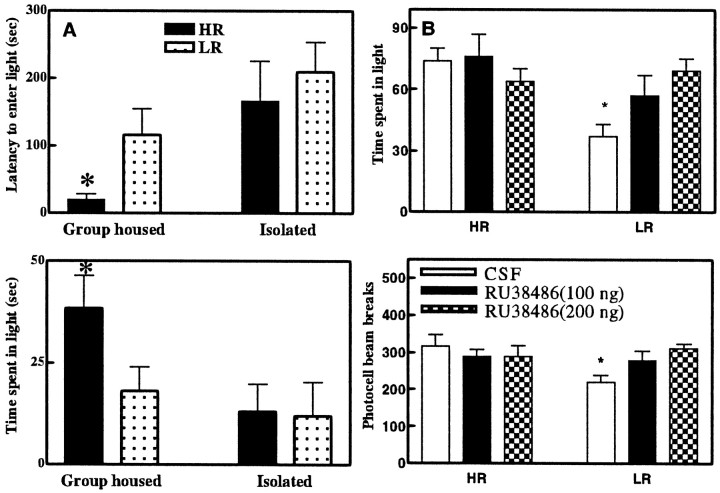
Fig. 3.
A, Effect of 1 week isolation stress on the anxiety-like behavior of HR and LR rats. Group-housed HR rats are quicker to first enter the light compartment (top graph), and they spend more time in this light (bottom graph). However, after 1 week of isolation, HR rats exhibit prolonged latencies to enter the light compartment and they spend less time in the light compartment. The behavior of the HR rats after 1 week of isolation stress does not differ from the behavior of the LR rats. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 for comparisons with the group-housed HR rats. B, Anxiety-like behavior in HR and LR rats in the light/dark boxes after microinjection of CSF or RU38486 in the hippocampus. Compared with CSF-treated LR rats, CSF-treated HR rats spent more time in the light box (top graph). The difference between LR and HR rats in the time spent in the light box disappeared with the microinjection of RU38486 at both doses (100 and 200 ng). Bottom graph, Locomotor response to the novel light/dark box environment after microinjection of CSF or RU38486 in the hippocampus. Compared with CSF-treated LR rats, CSF-treated HR rats are more active in the novel environment. The difference in locomotor activity between LR and HR rats disappeared after microinjection of RU38486 at both doses (100 and 200 ng). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p< 0.05. Comparisons are made between HR and LR CSF- or RU 38486-treated rats.