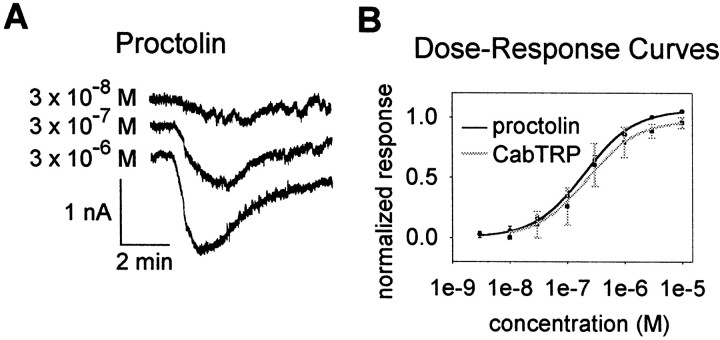
Fig. 7.
Dose–response curves for proctolin and CabTRP in the LP neuron. A, Representative voltage-clamp traces from bath application of varying concentrations of proctolin.B, Dose-response curves for proctolin (n = 5) and CabTRP (n = 3). For each individual experiment, peak currents were normalized to the largest response. Responses across all experiments were then averaged and plotted ± SE. Recordings were made using TEVC in the presence of 10 μm PTX and 0.1 μm TTX. The fits to the data points were done to the curve y =Imaxx/(Kd+ x), where x is the concentration of the applied peptide, Imax is the normalized maximal current, and Kd is the dissociation constant. For proctolin, Imax = 1.06 ± 0.01, and Kd = 2.02 ± 0.01 × 10−7m. For CabTRP, Imax = 0.97 ± 0.03, and Kd = 2.25 ± 0.29 × 10−7m.