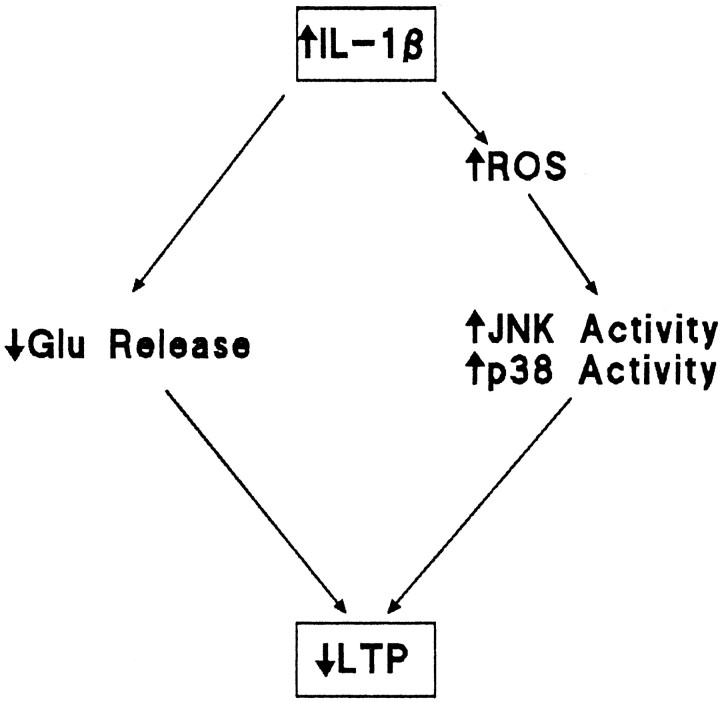
Fig. 8.
Scheme suggesting cascade of events leading to the IL-1β-induced impairment in LTP. Intracerebroventricular injection of IL-1β leads to an increase in reactive oxygen species production that increases activity of JNK and p38. We propose that glutamate release is compromised by activation of IL-1 receptors, one consequence of which is activation of these kinases, and that this inhibition of glutamate release significantly contributes to the IL-1β-induced impairment in LTP.