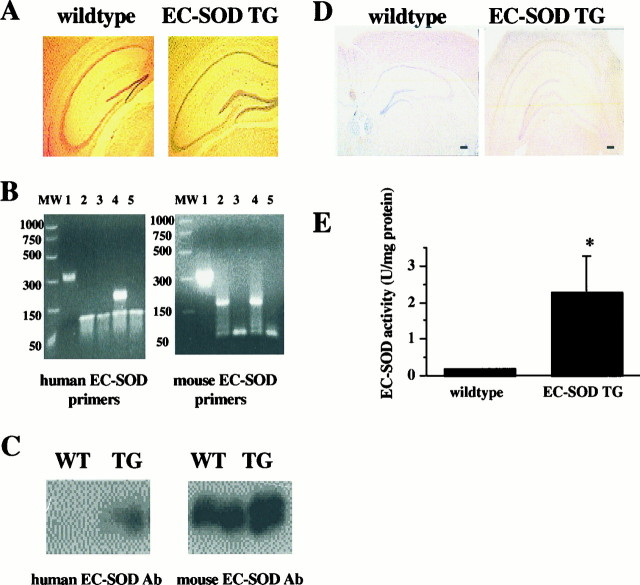
Fig. 1.
Anatomical and biochemical comparison of wild-type and EC-SOD transgenic mice. A, Nissl stains of sagittal sections through the hippocampus of wild-type (left) and EC-SOD transgenic (right) mice. B, RT-PCR of mouse hippocampal RNA. MW, Molecular weight marker; lane 1, RT-PCR kit positive control;lane 2, wild-type mouse hippocampal RNA; lane 3, wild-type mouse hippocampal RNA with RNase; lane 4, EC-SOD trangenic mouse hippocampal RNA; lane 5, EC-SOD transgenic mouse hippocampal RNA with Rnase.C, Western blot of hippocampal homogenates from wild-type (WT) and EC-SOD transgenic (TG) mice. The blots were probed with antibodies specific for either human EC-SOD (top) or mouse EC-SOD (bottom). D, Immunocytochemistry of either wild-type (left) or EC-SOD transgenic (right) mice showing diffuse expression of human EC-SOD in the hippocampi of EC-SOD transgenic mice. Scale bars, 200 μm.E, EC-SOD activity measured in hippocampal homogenates from wild-type and EC-SOD transgenic mice. Error bars indicate SEM for four determinations. *Statistical significance with a paired Student'st test (p < 0.05).