Fig. 1.
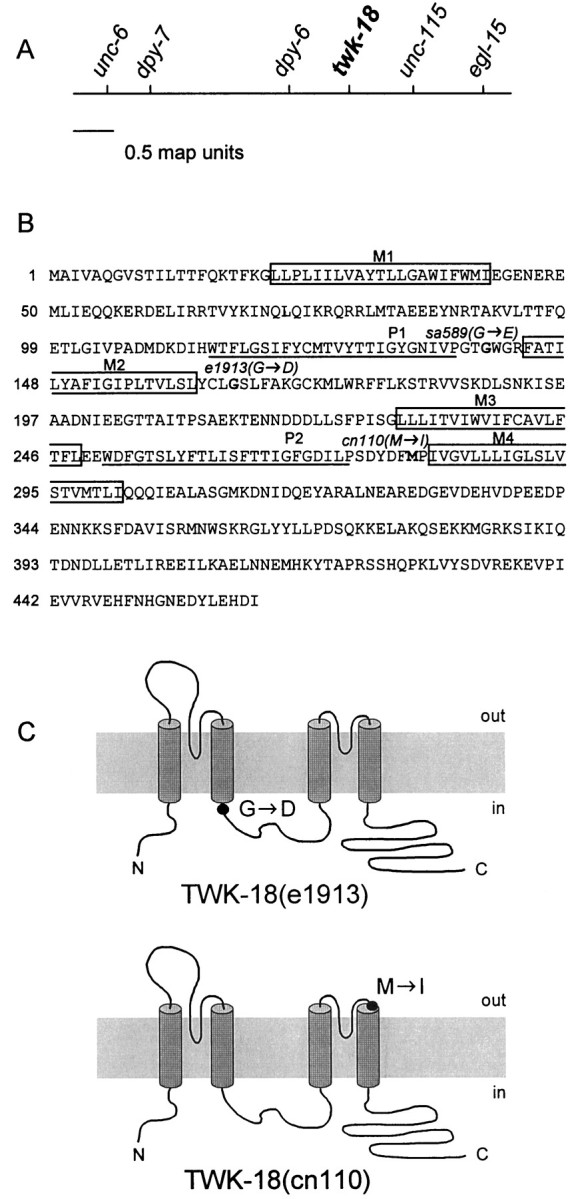
Identification of twk-18(e1913) andtwk-18(cn110). A, Genetic map of thetwk-18 gene. The center of the X chromosome is shown.twk-18(e1913) and twk-18(cn110) were mapped to the interval between dpy-6 andunc-115. The predicted potassium channel gene,twk-18, was sequenced from both mutants, and each had a missense mutation within its coding region. B, Amino acid sequence of TWK-18. The four predicted transmembrane domains areboxed and labeled M1–M4. The P regions are underlined and labeled P1 andP2. The amino acid residues mutated in thetwk-18 mutants are marked in bold, and the substitution is indicated for each allele. C, Amino acid changes identified in the mutant twk-18 alleles illustrated on a diagram showing the putative topology of TWK-18 subunits. In twk-18(e1913) animals, an aspartate residue is substituted for a highly conserved glycine at the intracellular boundary of M2 (top). In twk-18(cn110)animals, an isoleucine is substituted for a methionine residue at the extracellular boundary of M4 (bottom).
