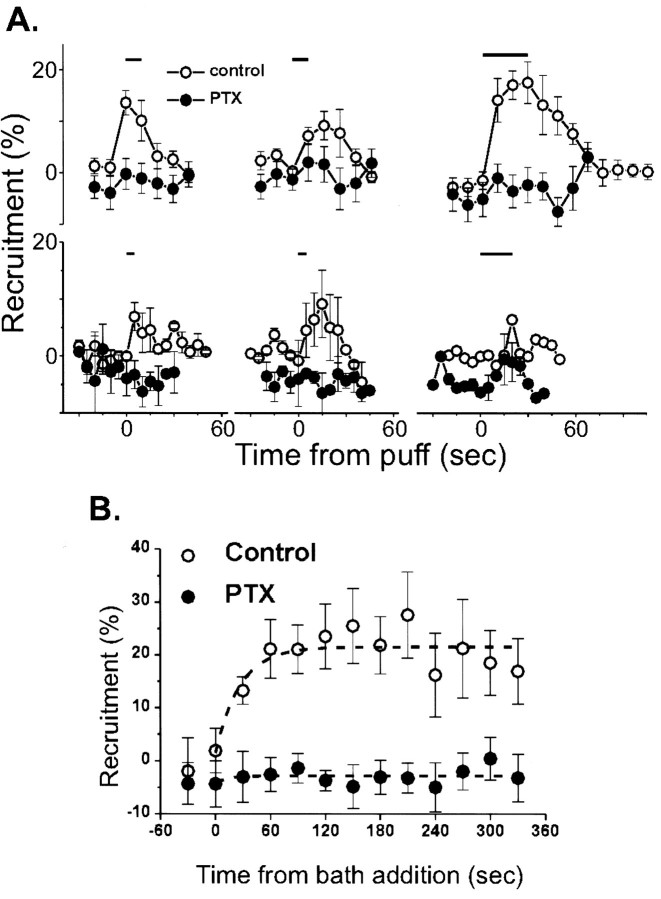
Fig. 3.
Effect of PTX pretreatment on adenosine-induced calcium current inhibition. A, Time course of calcium channel inhibition with puff application of transmitter (horizontal bar) with or without overnight PTX treatment. The effects of three consecutive trials given ∼1 min apart to each group of calyces are shown. Top series,Adenosine (10 μm) treatment (control,n = 6; PTX, n = 14).Bottom series, Treatment with a cocktail of substance P (0.5 μm), bradykinin (1 μm), neuropeptide Y (0.1 μm), and BRL52537 (1 μm; control, n = 4; PTX,n = 3). B, Bath application of adenosine. Current inhibition was monitored after the addition (t = 0) of adenosine (0.2 mm) to control (open symbols, n = 6) or PTX-treated (filled symbols,n = 6) calyces. In both A andB current inhibition is monitored by the percentage of prepulse recruitment.