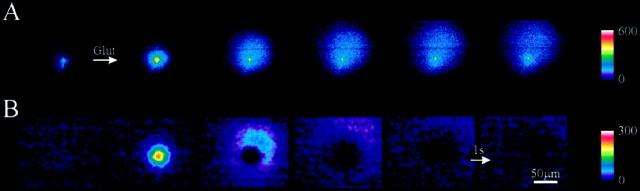
Fig. 6.
Passive diffusion of glutamate and NADH from a point source. To determine the spatial resolution of the glutamate imaging system we ejected glutamate (10 mm) from the tip of a pipette. A, A sequence of fluorescence images is shown during the ejection of glutamate (14 msec pressure pulse) from a pipette tip in a saline containing GDH and NAD+. Note that the fluorescence in the first image is attributable to fluorescence associated with the pipette tip, not to NADH in the bathing saline. B, The same images as shown inA were processed by subtraction of the previous image [n − (n − 1)] to obtain difference images (an image obtained before the first raw image inA was used in the subtraction to calculate the first difference image shown in B). Note these difference images clearly show the timing of appearance of new fluorescent molecules (see Results). Camera integration time, 500 msec.Arrow, 1 sec image interval. The color scale indicates linear pseudocolor representation of fluorescence intensity ranging from 0 to 600 in A and from 0 to 300 in B.