Fig. 2.
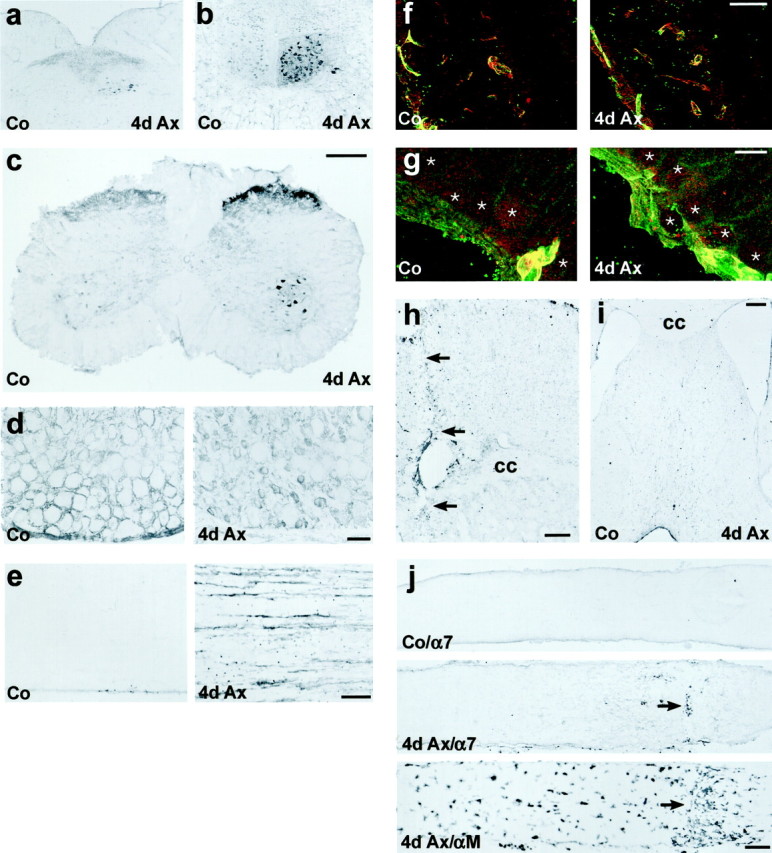
Enhanced α7 and β1 integrin immunoreactivity (IR) in different models of peripheral but not of central axotomy.a–e, Peripheral nerve transection. a, b,Axotomy of the vagal (a) or hypoglossal nerve (b) leads to a strong increase of α7-IR in the corresponding nucleus (4d Ax). c–e,Transection of the sciatic nerve also leads to strong α7-IR on the axotomized motoneurons and in the substantia gelatinosa in the lumbar spinal cord (4d Ax). d, In the normal DRG (Co), α7 is localized to satellite cells surrounding the sensory neurons. Sciatic axotomy leads to a disappearance of this staining and a strong increase of α7-IR on the small sensory neurons (4d Ax). e, α7 is also upregulated on the regenerating axons in the sciatic nerve (4d Ax).f–j, Transection of CNS axons. f, g,Immunofluorescence double labeling in the axotomized retina revealed a colocalization of α7 (red) and β1 (green) on blood vessels (yellow profiles), but no staining of both subunits on normal (Co) and axotomized retinal ganglion cells (4d Ax, asterisks). h, i, Cortical incision with resulting transection of the underlying corpus callosum (h; cc, arrows) and the septohippocampal tract (i) induced α7-IR on peritraumatic blood vessels but not on the axotomized pyramidal cells and septal neurons.j, α7 is also absent from the axons of normal (Co/α7) and axotomized (4d Ax/α7) RGCs. The arrow points to the transversal accumulation of peroxidase-positive leukocytes at the lesion site (4d Ax/α7). The optic nerve crush is also demarcated by the accumulation of αMβ2-positive macrophages in an adjacent section (4d Ax/αM, arrow). Scale bars:c (also applicable to a, b), h, j, 250 μm; d, e, i, 100 μm;f, 50 μm; g, 10 μm.
