Fig. 3.
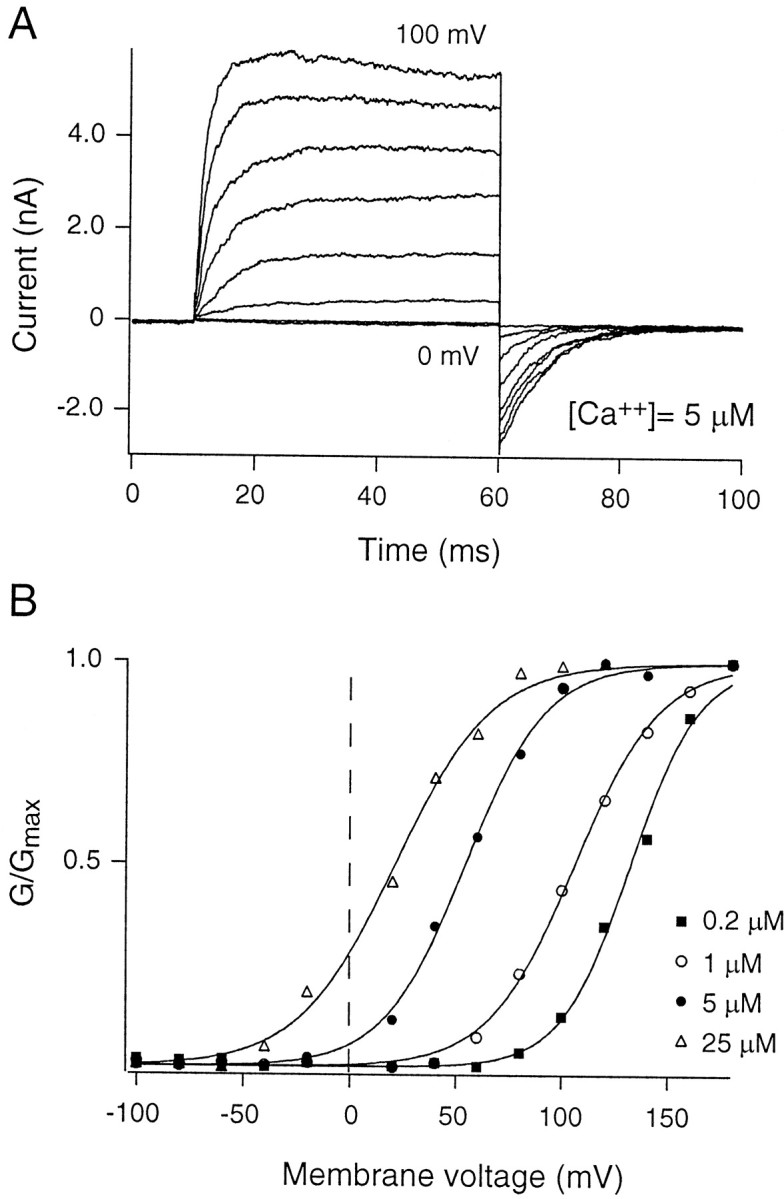
Gating of α0 channels. Inside-out patches from HEK293 cells containing BK channels formed by α-subunits alone (α0) were exposed to different concentrations of calcium. Voltage protocols used to test the steady-state open probability were designed to span the activation range of the channel for each calcium concentration. A, Currents from one inside-out patch exposed to 5 μmCa2+. The activation voltage ranges from 0 to +100 mV (in steps of 10 mV), and deactivating tail currents were measured at −50 mV. Instantaneous currents at the onset of the tail voltage were used as an estimate of the conductance of the channels in the patch.B, Four different calcium concentrations (0.2, 1, 5, and 25 μm) were tested.G/Gmax was fit with a Boltzmann distribution between closed and open states (Eq. 1). The leftward shift in G–V relationships with increasing concentrations of calcium on the “cytoplasmic” side of the channels illustrates the calcium and voltage dependence of the BK channel.
