Fig. 3.
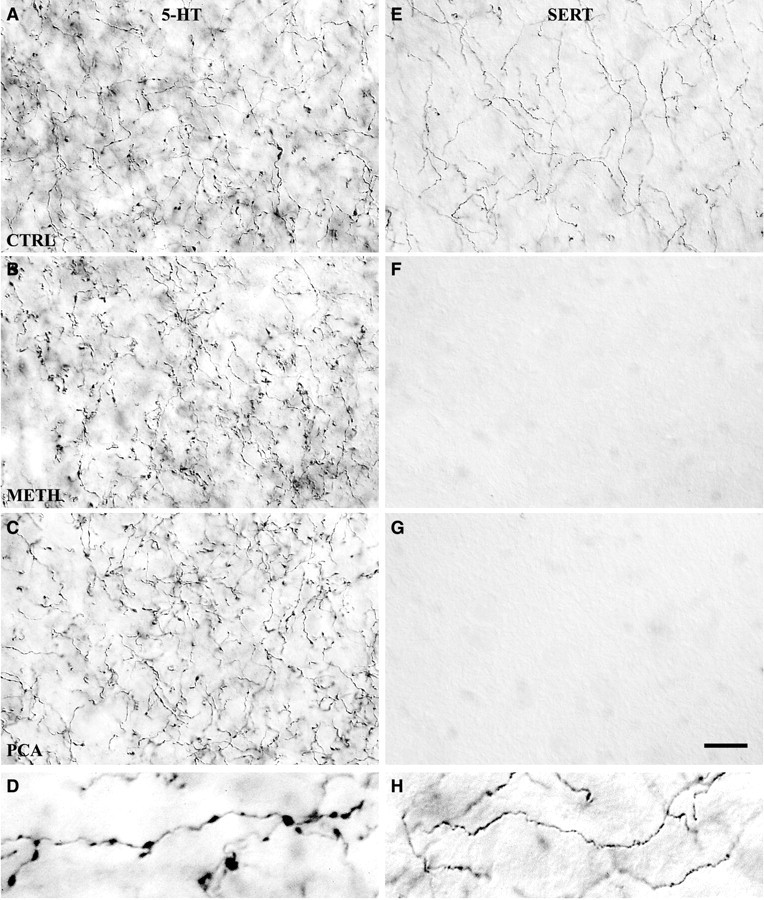
Two morphological types of 5-HT axons in caudal NAc shell differ in SERT expression and in response to Meth and PCA. High-magnification images show the effect of Meth (4 × 20 mg/kg) or PCA (2 × 10 mg/kg) on 5-HT-IR (A–C) and SERT-IR (E–G) axon terminals in the caudal shell of the nucleus accumbens. Most 5-HT axons in the NAc shell have large varicosities (D) and lack SERT expression; these axons are unaffected by either drug (A–C). In control rats, a smaller number of thin axons in the shell lack varicosities and express SERT (E,H); the SERT-IR axons are ablated by either drug (F, G). Drug-treated animals were killed 14 d after drug treatment, and sections were processed by ICC to demonstrate 5-HT or SERT expression. Images were photographed with a 100× oil immersion objective using DIC. Scale bar, 15 μm. Enlarged images in thebottom row (at twice the magnification) show examples of varicose 5-HT-IR axon terminals (D) or thin nonvaricose SERT-IR axon terminals (H).A, E, Saline-treated; B, F, Meth-treated;C, G, PCA-treated.
