Fig. 4.
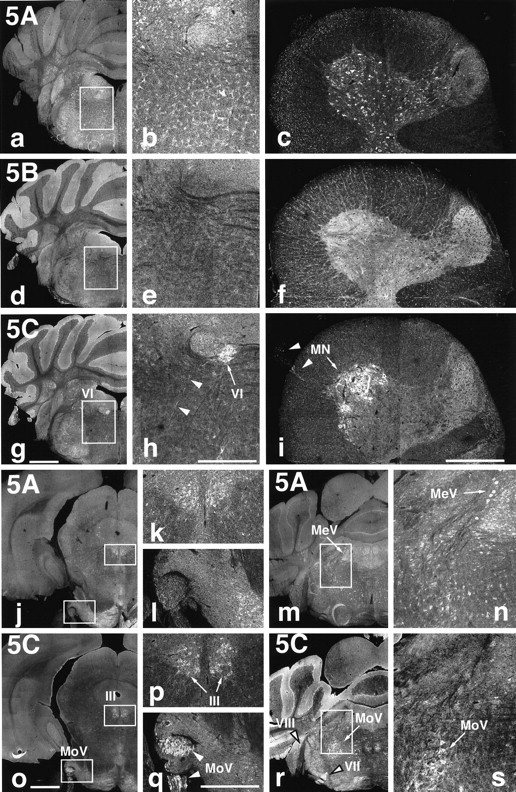
KIF5C is highly expressed in motor neurons. Localization of the three KIF5s in the brain and spinal cord.a–i, Immunofluorescence of brain frontal sections including the abducens nucleus (VI) [low magnification (a, d, g) and high magnification (b, e, h) of the boxed areas] and cross-sections of the spinal cord at the C7 level (c, f, i) after staining with anti-KIF5 antibodies (KIF5A, a–c; KIF5B, d–f; KIF5C, g–i). KIF5B was highly expressed in glial cells [mainly astrocytes (brain) and oligodendrocytes (spinal cord)] but was less abundant in neurons. KIF5A and KIF5C were localized to neurons but showed different expression patterns. KIF5A was found at similar levels of expression in various kinds of neurons, whereas KIF5C was highly expressed in motor neurons both in the brain (VI) and in the spinal cord (MN). j–s, Distribution of KIF5A (j–n) and KIF5C (o–s) in the sections containing several cranial nerves. KIF5A was expressed equally among neurons as described above. However, prominent expression of KIF5C was observed in motor [oculomotor (III), motor trigeminal (MoV), and facial (VII) nerves], but the expression was weaker in the sensory [mesencephalic trigeminal (MeV) and vestibulocochlear (VIII)] neurons. k,l, n, p, q, and s represent higher magnifications of theboxed areas in their left panels, respectively. Note the higher expression of KIF5A in sensory (MeV) than in motor (MoV) neurons, in contrast to KIF5C. Arrows andarrowheads indicate cell bodies and axons, respectively. Scale bars: a, d, g,j, m, o, r, 1 mm (low magnifications); b, c,e, f, h, i,k, l, n, p,q, s, 0.4 mm (high magnifications).
