Fig. 2.
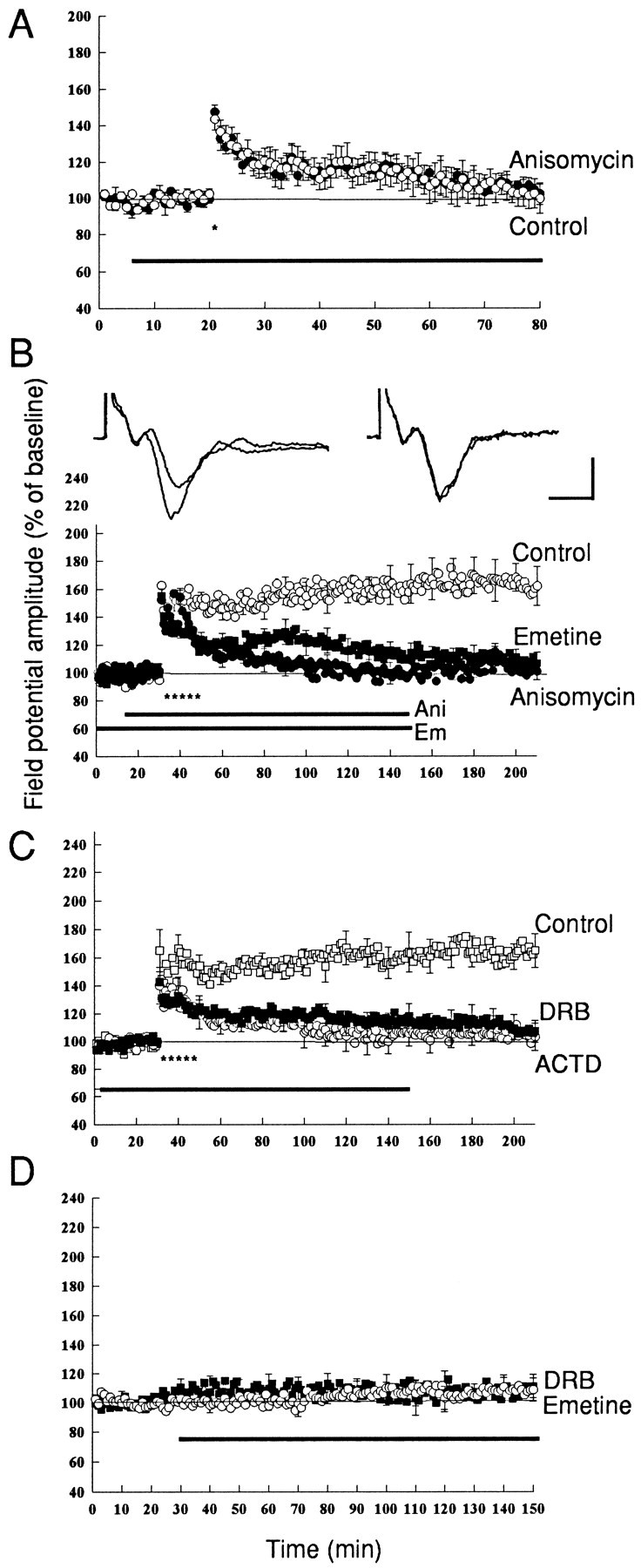
Inhibitors of protein and mRNA synthesis block L-LTP in the amygdala. A, Anisomycin has no effect on E-LTP induced by a single tetanus (100 Hz, 1 sec, indicated by theasterisk). Open circles, Control experiments (n = 5); filled circles, LTP in the presence of anisomycin (20 μm; n = 6). B, Anisomycin blocks L-LTP induced by five train of tetanus. Anisomycin (20 μm) or emetine (100 μm) was applied before the tetanus and perfused for 60–90 min. Open circles, Control experiments (n = 5); filled circles, LTP in the slices treated with anisomycin (n = 6);filled squares, LTP in slices treated with emetine (n = 7). Representative field potentials before and 3 hr after tetanus in control (left) and in anisomycin-treated slices (right) are shown at the top of this panel. Calibration: 5 msec, 0.5 mV. C, Transcriptional inhibitors block L-LTP. ACTD (40 μm) or DRB (100 μm) was applied 30–60 min before the tetanus and perfused for 2 hr. LTP decayed to the baseline in ∼90 min after tetanus in the presence of ACTD (open circles;n = 6) and DRB (filled squares; n = 7). D, Emetine (100 μm, open circles;n = 4) and DRB (100 μm, filled squares; n = 4) have no effect on the baseline synaptic response.
