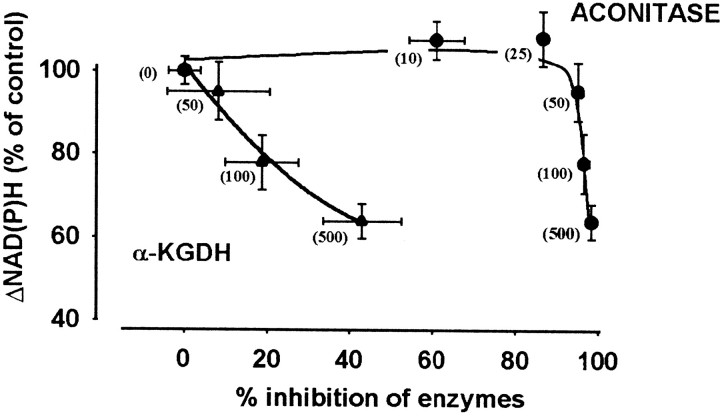
Fig. 5.
Relationship between inhibition of aconitase or α-KGDH and decrease in the rotenone-induced NAD(P)H fluorescence. Decreases in the rotenone-induced NAD(P)H signal (data in Fig. 4,curve b) are shown as a function of percentage inhibition of aconitase (derived from Fig. 1) or α-KGDH (from Fig.2a) as measured after incubation with H2O2 for 5 min. H2O2concentrations (in micromoles) are indicated inbrackets. We have shown in separate control experiments (data not shown) that BCNU at 200 μm concentration has no effect on the activities of aconitase or α-KGDH, nor does it influence the effect of H2O2 on these enzymes. Data are average of five [for NAD(P)H measurement] or eight (for enzyme assays) determinations ± SEM.