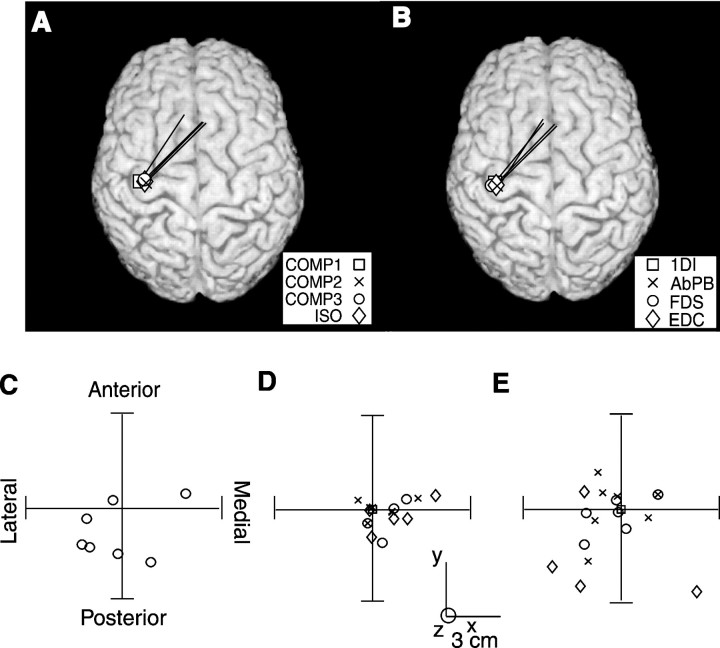
Fig. 7.
Cortical source analysis of coherent MEG activity.A, B, Single subject data showing the direction and strength of the current dipole on the subject's surface-rendered magnetic resonance image for MEG–1DI EMG coherence during the second hold period for the four task conditions COMP1, COMP2, COMP3, and ISO (A), and the MEG–EMG coherence for the four muscles recorded during the second hold period (B). C shows the distances of the cortical sources of the MEG–1DI coherence spectra during the first hold period relative to those during the second hold period of the task performed under COMP1 conditions. Each point represents a different subject. D, The distance of the sources of the MEG signal with the highest level of coherence signals for MEG–AbPB (×), MEG–FDS (○), and MEG–EDC (⋄) pairs relative to those for the MEG–1DI pair during the second hold period under COMP1 conditions. Each point represents a different subject.E, The distance of cortical sources for the MEG–1DI coherence spectra during Hold 2 under COMP2 (×), COMP3 (○), and ISO (⋄) conditions relative to those for the COMP1 condition. Eachpoint represents a different subject.