Fig. 6.
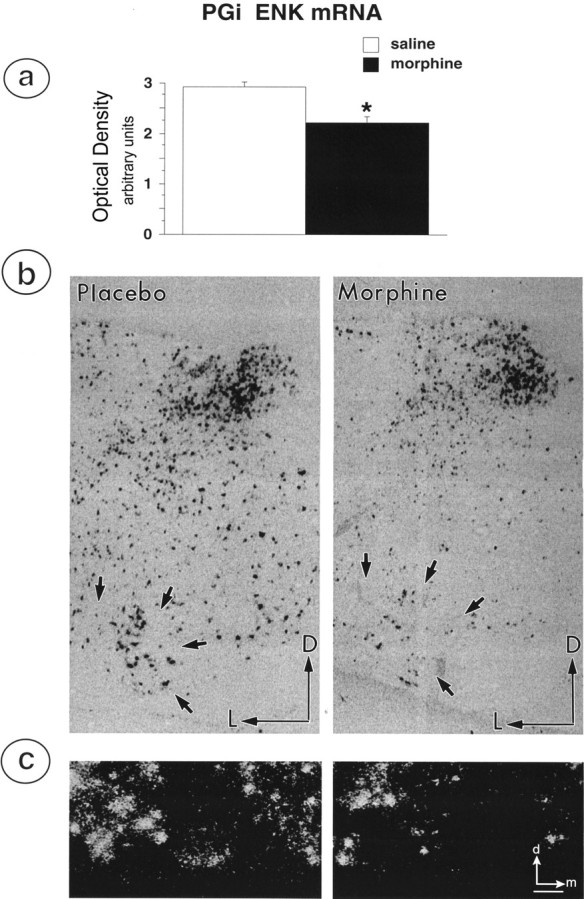
Brain sections through the medulla oblongata of morphine- and placebo-treated rats were processed for in situ hybridization of mRNA for PPE using a plasmid generously provided by Dr. S. Sabol (National Institutes of Health).a, Graphic illustration depicting the effects of morphine treatment on average optical density for ENK mRNA hybridization signal in the PGi. Chronic morphine treatment caused a statistically significant decrease in PPE mRNA expression in PGi neurons. b, Representative examples of coronal sections of medullary sections containing the PGi and processed for in situ hybridization of ENK mRNA expression in placebo- and morphine-treated rats. Straight black arrows indicate location of PGi neurons in the ventral medulla. Arrowspoint dorsally (D) and laterally (L). c, High-magnification image of in situ hybridization labeling of PGi neurons from a placebo-treated (left) and morphine-treated (right) rat. Arrows point dorsally (d) and medially (m). Expression of mRNA for PPE is reduced in samples obtained from morphine-treated rats. Scale bar, 100 μm.
