Fig. 6.
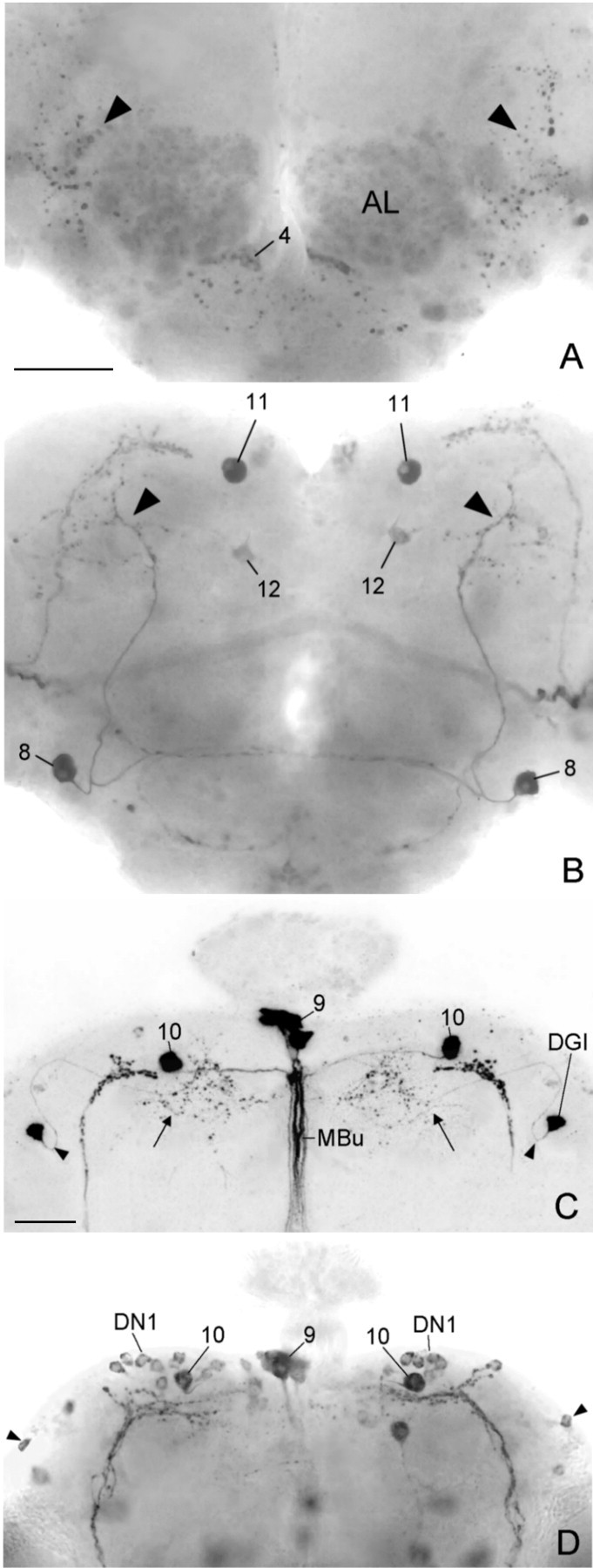
Ectopic PDF in the central brains of three different gal4; UAS-pdf lines that express PDF only in subsets of the neurons that were found in theelav-gal4; UAS-pdf line. A typical Mz1525-gal4; UAS-pdf brain is depicted from an anterior (A) and posterior (B) plane of focus. This brain stemmed from the experimental animal with arrhythmic activity pattern shown in Figure 7C. Ectopic PDF was found in only a few neuron pairs in this brain. The most prominent one was neuron 8, which showed arborizations in the anterior brain (arrowheads in A) as well as in the dorsolateral posterior brain (arrowheads in B). The somata of neuron pair 11 were also strongly stained, but their arborizations into the dorsolateral brain and down the median bundle (see Fig. 10A) were not revealed. Weak staining was found in the soma of neuron 12 and in neurons of cluster 4 plus their putative arborizations in the antennal lobes (AL). In the lineMz1172-gal4; UAS-pdf(C), neuron pair 10 was prominently revealed together with neurons in the pars intercerebralis (cluster 9). All of these cells projected down the median bundle (MBu). The other arborizations (arrow) in this brain stemmed from the dorsal giant interneuron (DGI). The arrowheadspoint to the characteristic bend of the neurite close to its soma (cf.Ito et al., 1997). In the per-gal4; UAS-pdf line (D), the first group of dorsal neurons (DN1) was clearly stained. Neuron10 was located among these cells; whether it belongs to the DN1 is unclear. The DN2 neurons were not revealed in this particular brain, but some DN3 appear to be stained (arrowhead). PDF was also found in some neurons that naturally do not express per and tim as in the neurons of cluster 9 [compare Table 1 and Kaneko (1998)]. Scale bars: (shown in A) A,B, 50 μm; (shown in C)C, D, 50 μm.
