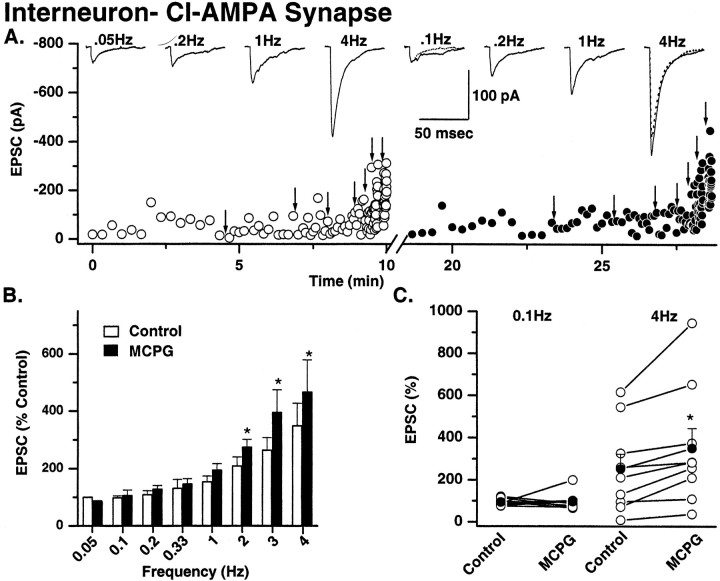
Fig. 7.
Mossy fiber→interneuron CI AMPA synapses: frequency-dependent facilitation and modulation by metabotropic glutamate receptors. A, Single representative experiment showing the frequency-dependent facilitation of mossy fiber→interneuron CI AMPA EPSC amplitude. Protocols identical to that described in Figure 6 were used. Open circles represent control recording conditions; solid circles are EPSC amplitudes in MCPG (0.5 mm). After a return to the control frequency, the solution was then exchanged for one containing MCPG (0.5 mm), and the experiment was repeated (solid circles). MCPG enhanced the amplitude of mossy fiber→interneuron CI AMPA EPSCs only at frequencies of 2 Hz and above. Traces above thedot plots show averaged EPSCs from four representative frequencies. The EPSC amplitude in the control (dotted traces) is superimposed on the 0.1 and 4 Hz data to illustrate the frequency-dependent enhancement of EPSCs by MCPG. B, Summary histogram from six experiments showing the mean EPSC facilitation (data normalized to 0.05 Hz data). Note that the maximum facilitation at 4 Hz is less pronounced than that observed at mossy fiber→pyramidal cell synapses (350.6 ± 94.3% of control vs 1049 ± 260%, respectively; see Fig. 6). MCPG significantly enhanced EPSC amplitude in all experiments only at 2 Hz and above.C, Plot of data from all experiments at 0.1 and 4 Hz in control and MCPG to illustrate that despite the wide range of frequency-dependent facilitation across all experiments MCPG significantly enhanced transmission only at high and not low frequencies in any experiment.