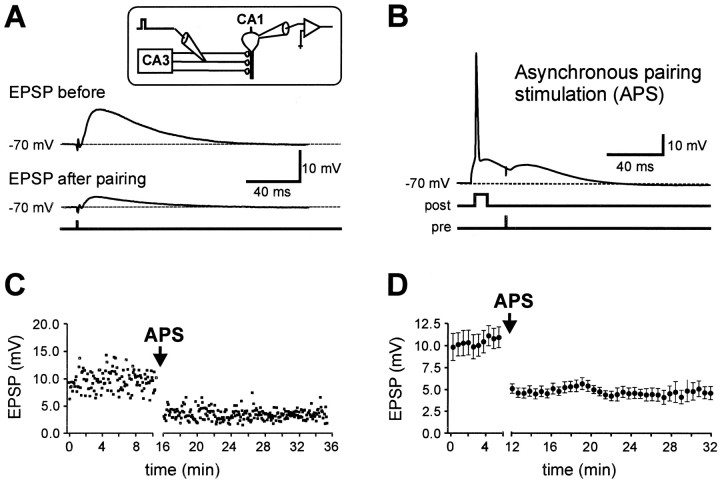
Fig. 1.
Associative LTD induced by asynchronous pairing of presynaptic and postsynaptic action potentials in CA1 pyramidal neurons. A, Current-clamp whole-cell recording from a CA1 pyramidal neuron. EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the Schaffer collateral pathway with 200 μsec voltage pulses applied through the stimulation pipette (inset). The EPSP amplitude was significantly decreased by asynchronous pairing of presynaptic and postsynaptic activity. Traces shown were taken immediately before and 15 min after asynchronous pairing.B, For the APS, a single action potential was evoked in the postsynaptic CA1 pyramidal neuron by current injection (700 pA, 5 msec). Twenty milliseconds after the onset of the current injection, an EPSP was evoked. This pairing was repeated 360 times at a frequency of 0.3 or 1 Hz. C, The EPSP amplitude during a single representative experiment is plotted against time. D, The mean EPSP amplitude is plotted against time (n= 17). The APS induction paradigm was applied at the time indicated by the arrow.