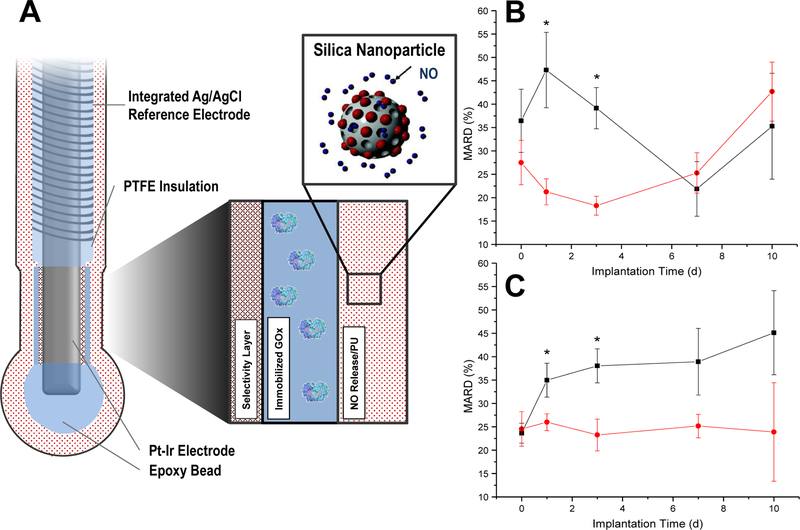
Figure 10.
Schematic of needle-type electrochemical glucose biosensor (A). The sensors were modified to store NO by doping NO-releasing silica nanoparticles into the outermost, glucose flux-limiting polyurethane layer. The graphs in (B, C) display the in vivo sensor numerical accuracy (mean absolute relative deviation) of NO-releasing (black, square) and control (red, circle) for the N-diazeniumdiolate- (B) and S-nitrosothiol-based (C) membranes. Figure adapted with permission from Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86, Soto, R. J.; Privett, B. J.; Schoenfisch, M. H. “In vivo analytical performance of nitric oxide-releasing glucose biosensors,” pages 7141–7149. Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society.