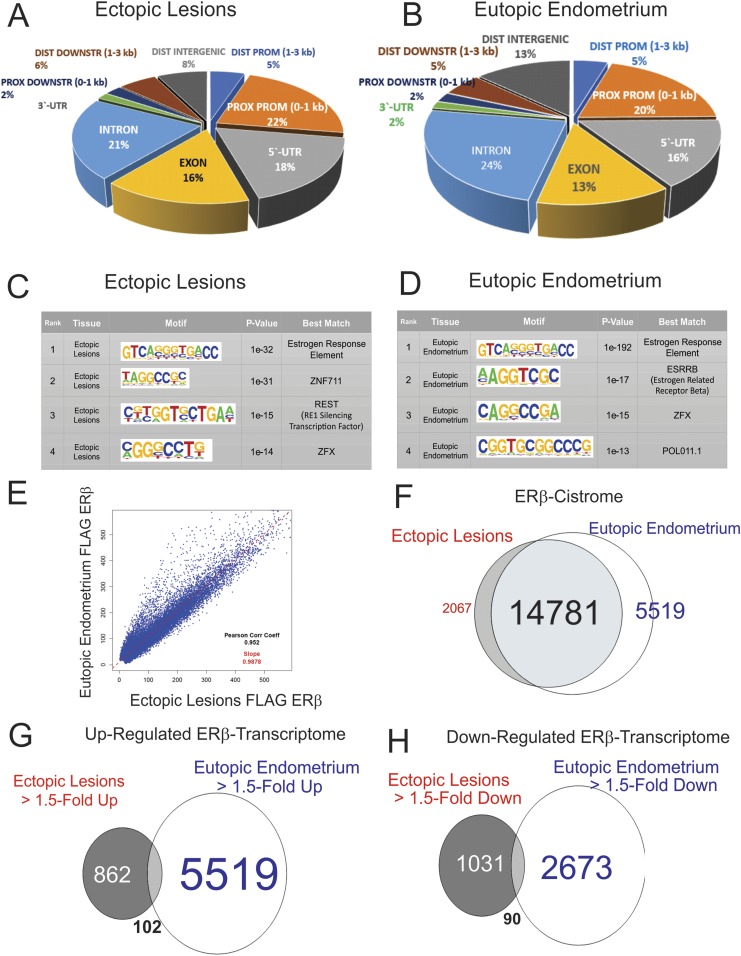
Figure 4.
ERβ cistrome in ectopic lesions and the eutopic endometrium of mice with endometriosis. (A and B) Distribution of ERβ-occupied sites in the genome of ectopic lesions (A) and the eutopic endometrium (B). (C and D) Determination of the sequence recognized by ERβ in ectopic lesions (C) and the eutopic endometrium (D). The MEME method (http://meme-suite.org) was used for identification of enriched sequences and is displayed with a correlation of the size of the character and the rate of enrichment. P value means the probability de novo-enriched sequences obtained from ChIP-seq– are matched to the displayed WebLogo and known consensus motifs by chance. (E) Peak correlation scatterplot for the tag of FLAG-tagged ERβ ectopic lesions against the eutopic endometrium. (F) Venn diagrams depicting the overlap of the tag of FLAG-ERβ within the upstream 5 kbp, transcription start site 1 kbp, 5′ untranslated region, and first intron between ectopic lesions and the eutopic endometrium. (G and H) Venn diagrams depicting the overlap of 1.50-fold-upregulated (G) or -downregulated (H) gene expression between ectopic lesions and the eutopic endometrium compared with their control. DIST DOWNSTR, distal downstream; DIST PROM, distal promoter; PROX DOWNSTR, proximal downstream; PROX PROM, proximal promoter; UTR, untranslated region; ZNF, zinc finger protein; ZFX, zinc finger protein x-linked.