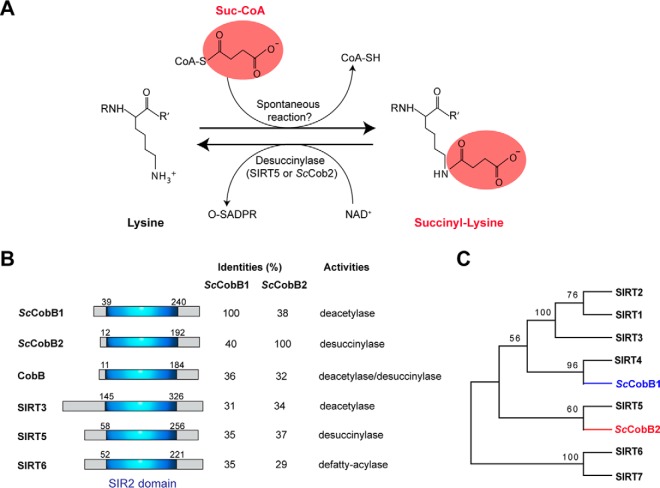
Fig. 1.
Bioinformatics analyses identify two different sirtuin proteins in S. coelicolor. (A) The chemical structure of succinylated lysine. Substrates and reactions of succinylation or desuccinylation of lysine are shown correspondingly. While desuccinylation can be catalyzed by desuccinylases, the specific succinyltransferase responsible for succinylation has not been identified yet. Spontaneous succinylation occurs by succinyl-CoA treatment as reported (15). O-SADPR: 2′-O-succinyl-ADP-ribose. (B) Similarity comparison of ScCobB1 or ScCobB2 to the mammalian sirtuins and the E. coli deacylase CobB. Schematic representation of the sirtuin proteins shows a conserved silent information regulator 2 domain. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of sirtuin proteins using MEGA software. S. coelicolor ScCobB2 showed an evolutionarily closer relationship to the desuccinylase Sirt5 rather than the deacetylases Sirt1–3 of mammalian cells. The sequences of human sirtuins were obtained from NCBI at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.