Figure 4.
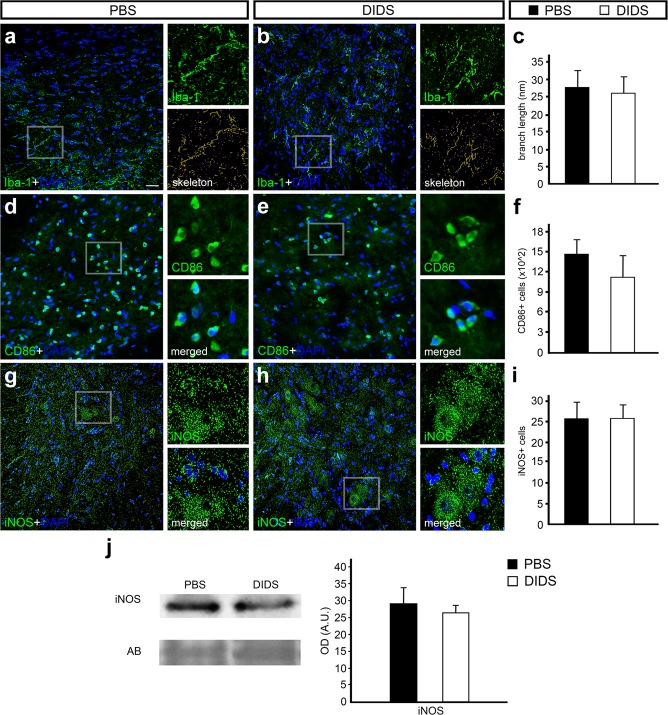
Immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis of ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1), cluster of differentiation 86 (CD86), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) counterstained with 4′-6-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) in transverse sections of rat spinal cord treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid (DIDS) 24 h after injury. Representative images from the ventral region of (a) PBS- and (b) DIDS-treated groups stained with Iba-1 (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue), with high magnification view of the respective selected area and tagged skeleton showing its voxels. (c) Graph indicating the average branch length of Iba-1-positive cells in PBS- and DIDS-treated groups. Representative images from the ventral region of (d) PBS- and (e) DIDS-treated groups stained with CD86 (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue), with high magnification view of the respective selected area. (f) Graph indicating the number of CD86-positive cells in PBS- and DIDS-treated groups. Representative images from the ventral region of (g) PBS- and (h) DIDS-treated group stained with iNOS (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue), with high magnification view of the respective selected area. (i) Graph indicating the number of iNOS-positive cells in PBS- and DIDS-treated groups. (j) Representative iNOS and amido black (AB) bands of spinal cord samples from PBS- and DIDS-treated animals. Quantification of the optical density of iNOS bands, comparing PBS- and DIDS-treated animals. Bars represent standard error of the mean. Scale bar: 50 μm.