Figure 1.
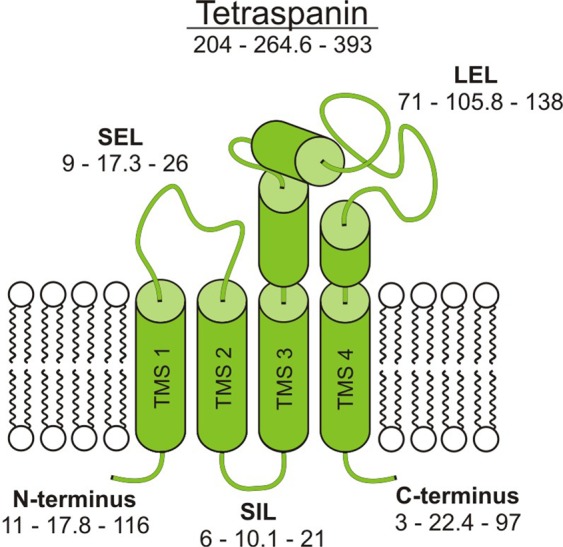
Conventional tetraspanin topology. Depicted is the typical topology of a tetraspanin. Intracellular domains include the N-terminus, the small intracellular loop (SIL), and the C-terminus, which are all short (for exceptions see Table S1). At the extracellular site, a small extracellular loop (SEL) connects transmembrane segment 1 (TMS1) and TMS2 and a large extracellular loop (LEL) TMS3 and TMS4. For the complete tetraspanin and its different segments, the three numbers (xx-yy-zz) indicate the sequence lengths of the shortest sequence (xx), the average sequence (yy) and the longest sequence (zz) (for details see Table S1).
