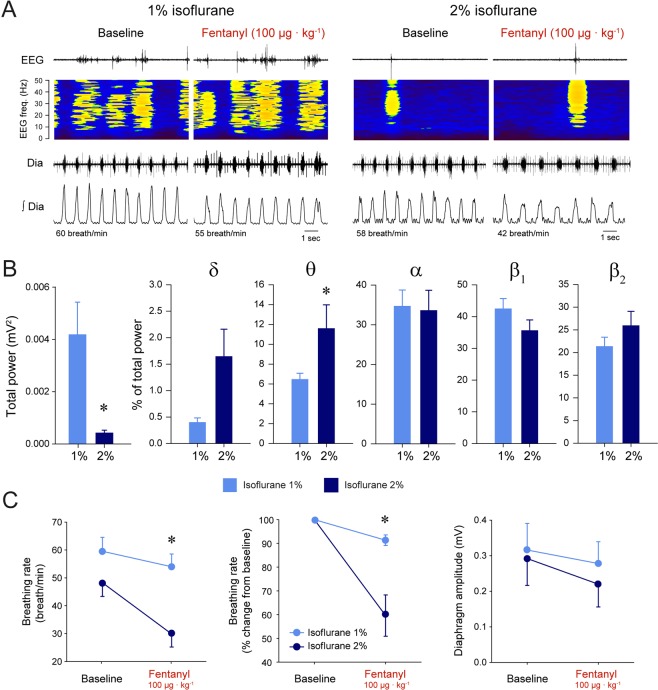
Figure 6.
Respiratory rate depression by systemic fentanyl at different levels of anaesthesia. (A) Fentanyl (100 µg · kg−1) injection in an anesthetized rat with 1% isoflurane moderately decreased respiratory rate. The same injection of fentanyl in the presence of 2% isoflurane substantially decreased respiratory rate. (B) Increased isoflurane levels decreased total electrocortical power between 0–50 Hz. More detailed analysis identified that increased isoflurane decreased θ powers (n = 5), without significantly changing the other frequency bands. (C) Respiratory rate reduction was more pronounced at 2% of isoflurane compared to 1%. There were no significant differences between the reductions of diaphragm amplitude by fentanyl observed at the two isoflurane levels. * indicates values significantly different between isoflurane levels with P < 0.05. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.