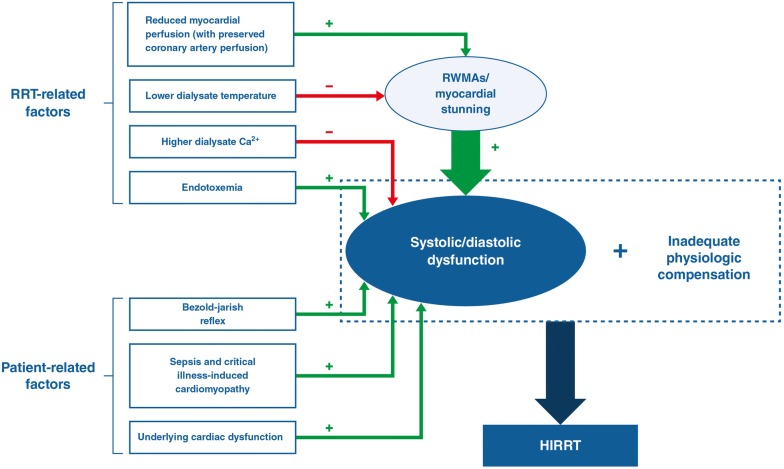
Fig. 3.
Contributors to cardiac dysfunction and HIRRT in critically ill patients with AKI requiring RRT. Both RRT and patient-related factors are implicated, in the presence of inadequate physiologic compensation. RRT induces transient episodes of reduced myocardial perfusion, leading to myocardial stunning, which is seen as regional wall motion abnormalities (RWMAs). UF and osmolar shifts can induce hypovolemia which can precipitate a Bezold–Jarisch reflex. Patient factors include underlying cardiac disease, critical illness and associated treatment (mechanical ventilation, fluid and vasopressors) and complications of critical illness such as bowel ischemia which itself can be exacerbated by HIRRT (not shown)