Figure 4.
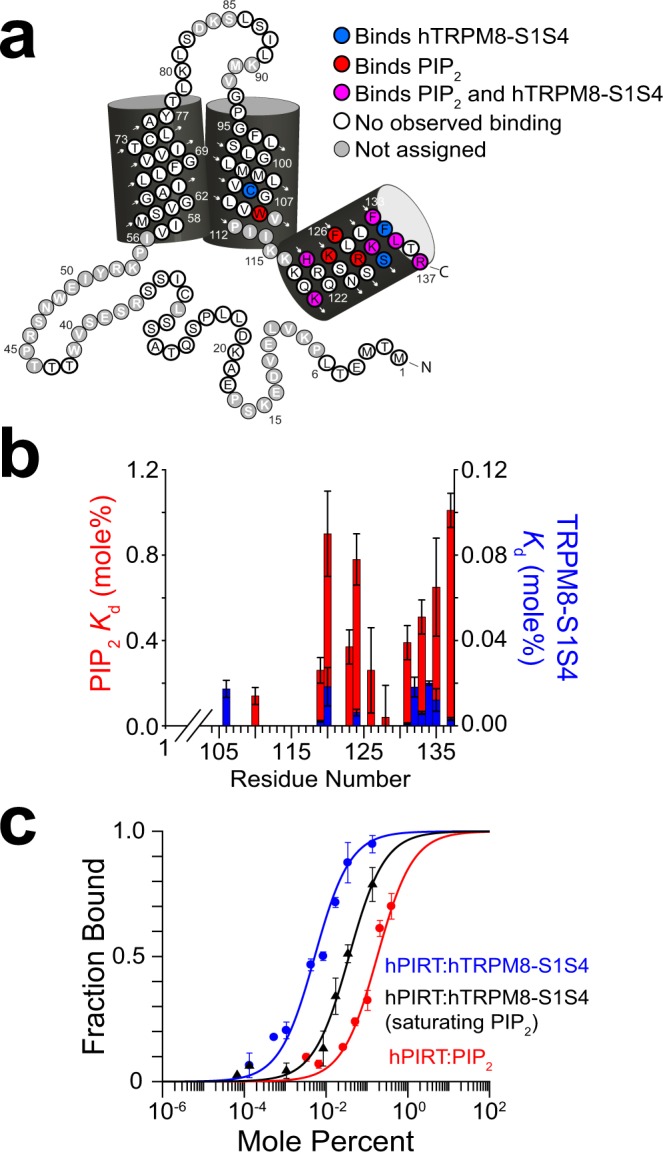
Competitive PIRT binding between PIP2 and TRPM8-S1S4. (a) NMR-detected titrations show hPIRT residues that bind both to PIP2 and hTRPM8 (magenta) are generally localized to the intracellular amphipathic helix. Residues that exclusively bind PIP2 (hTRPM8-S1S4) are colored red (blue). The overlapping binding regions indicate a competitive interaction for hPIRT. (b) Comparative binding affinities between PIP2 and the hTRPM8-S1S4 domain to hPIRT show overlapping binding sites and a higher hPIRT affinity for hTRPM8-S1S4. (c) MST measurements highlight the apparent competitive binding relationship between hPIRT, hTRPM8-S1S4, and PIP2 suggested by the NMR data. When hPIRT is titrated with the TRPM8-S1S4 domain in the presence of saturating PIP2, the affinity curve shifts rightward, indicative of competition. MST Kd values are 5.3 ± 0.4, 36.5 ± 0.5, and 180 ± 60 millimole percent for hPIRT:hTRPM8-S1S4, hPIRT:hTRPM8-S1S4 + PIP2, and hPIRT:PIP2 respectively.
