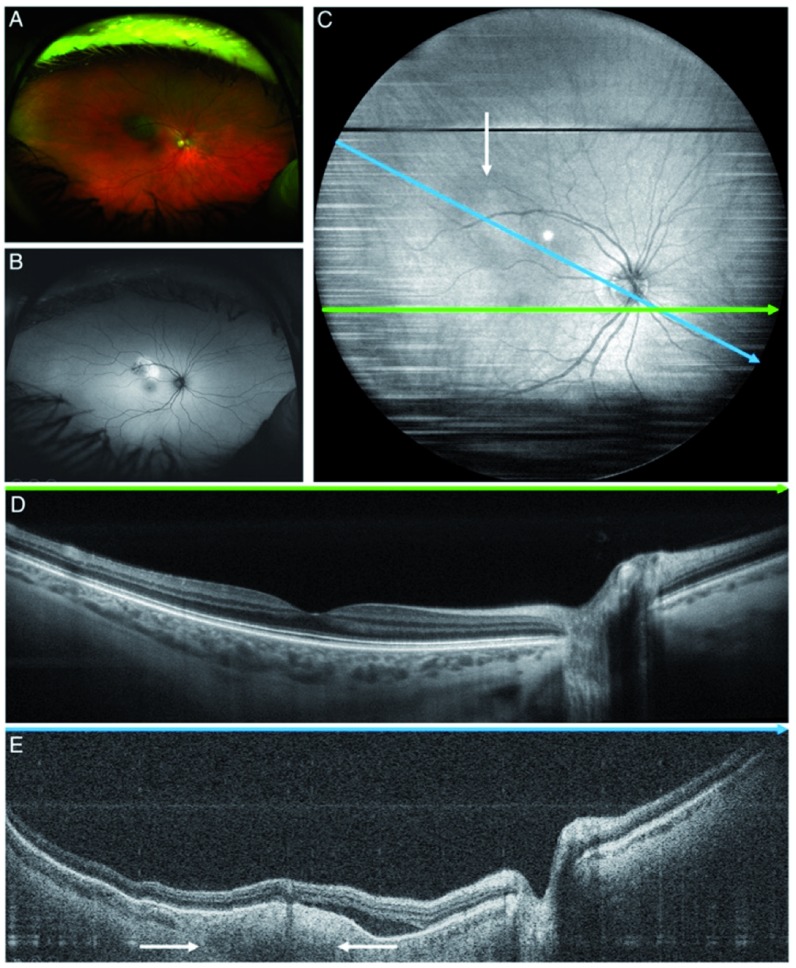
Figure 1. Wide field of view image of choroidal nevus (white arrows).
Images used with permission from Mcnabb et al. 7. A) Red/green and B) autofluorescence scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. C) Wide field of view swept-source optical coherence tomography (OCT) B-scan projection, blue line corresponding to position of image D), which demonstrates normal optic nerve, fovea, and retinal layers. E) OCT corresponding to green arrow demonstrating choroidal nevus with overlying drusen, loss of choriocapillaris, and associated subretinal fluid.