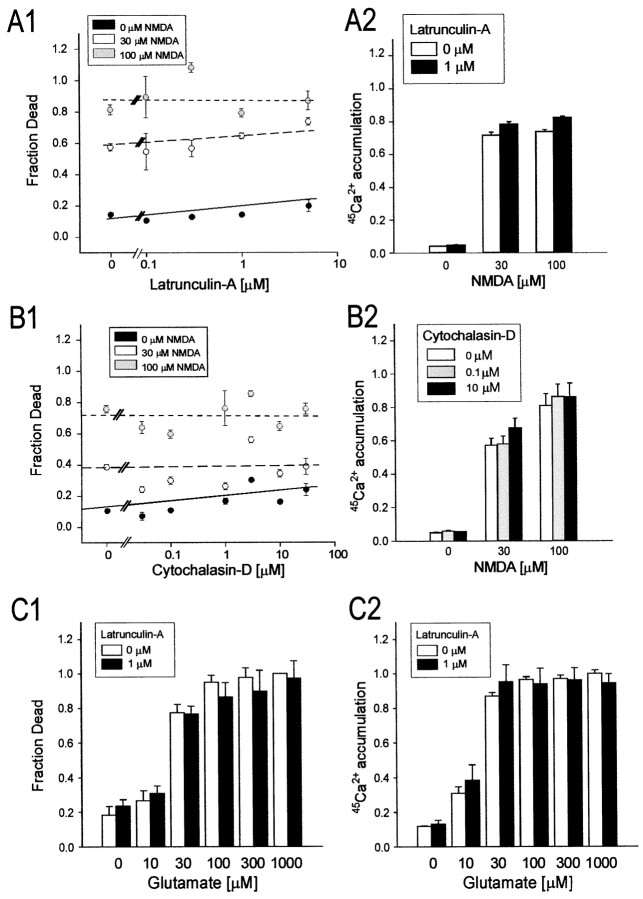
Fig. 6.
Disrupting F-actin has no impact on excitotixicity or neuronal Ca2+ loading evoked by exogenous NMDA or l-glutamate. Cultured cortical neurons were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of latrunculin-A (0–5 μm) or cytochalasin-D (0–30 μm) before undergoing exposure to 0, 30, or 100 μm NMDA (A, B) or 10–1000 μml-glutamate (C) for 60 min (in 2 μm nimodipine and 10 μm CNQX; see Materials and Methods). The cultures were then maintained for a further 23 hr to measure neuronal survival (A1–C1) or used for45Ca2+ accumulation measurements (A2–C2). A, Effects of treatment with latrunculin-A on NMDAR-mediated excitotoxicity (A1) and45Ca2+ loading (A2).B, Effects of treatment with cytochalasin-D on NMDAR-mediated excitotoxicity (B1) and45Ca2+ loading (B2).C, Effect of treatment with 1 μmlatrunculin-A on glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity (C1) and 45Ca2+ accumulation (C2). Symbols in A1 andB1 represent the mean survival (± SE) of 4–64 cultures per experimental condition, obtained from at least two (usually 4–6) different platings. The lines indicate the least-squares linear regression curves obtained for each NMDA concentration.Columns in A2 and B2represent the mean (± SE) 45Ca2+accumulation averaged from 16–36 cultures obtained from 4–6 different culture platings. Columns in C1 and C2were obtained from 16 cultures per condition pooled from two separate platings. Error bars are shown where they exceed symbol size.