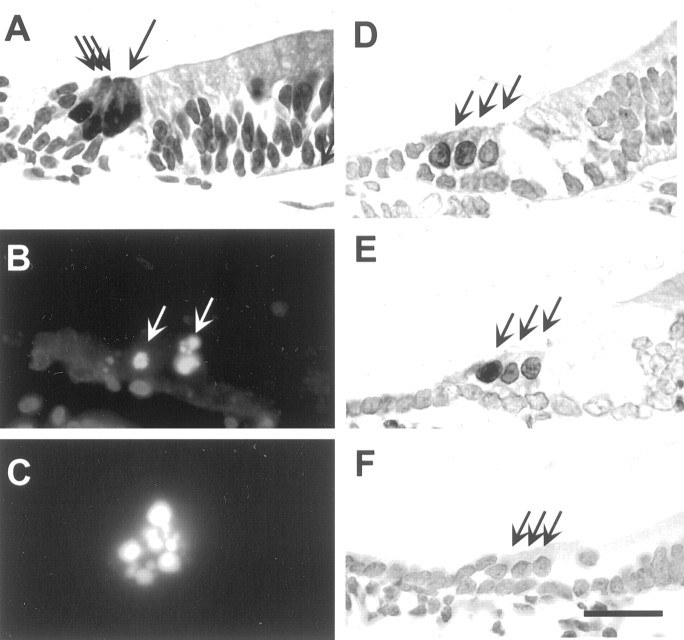
Fig. 1.
Hair cell death and JNK and c-Jun phosphorylation in neomycin-exposed (100 μm) cochlear explants of neonatal rats. The specimens were embedded in paraffin and cut in transverse (midmodiolar) plane. A, One row of calbindin-immunoreactive inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells (arrows) are seen in nonexposed explants. B, TUNEL-stained outer hair cell nuclei (arrows) are seen in cultures exposed to neomycin for 12 hr. C, Higher magnification of an outer hair cell nucleus showing TUNEL-positive DNA fragmentation. D, E, Phospho-JNK and phospho-c-Jun immunolabeling, respectively, are found in the nuclei of hair cells (arrows) exposed to neomycin for 6 hr. F, Phospho-c-Jun-immunoreactive hair cells are not seen in cultures coincubated with neomycin and CEP-1347 (500 nm) for 6 hr. Arrows point to hair cells. Scale bar: A,B, D–F, 27 μm; C, 10 μm.