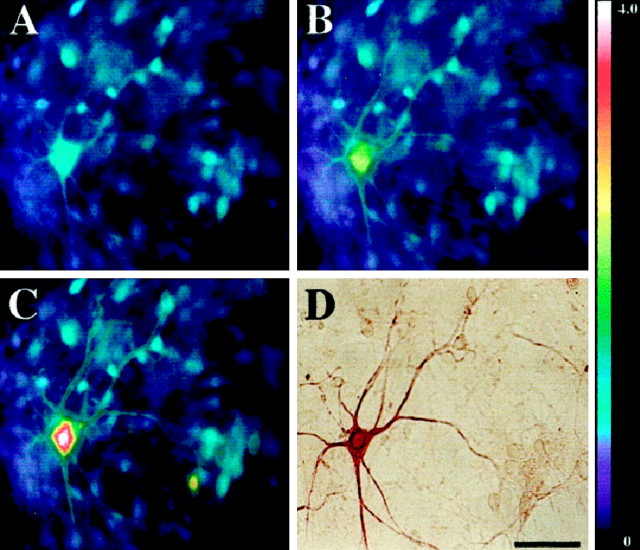
Fig. 3.
AMPA exposure triggers mitochondrial Ca2+ loading in motor neurons. Spinal cultures were loaded with Fura-2FF, and basal [Ca2+]i levels were recorded before cultures were exposed to an initial AMPA pulse (50 μm + 10 μm MK-801 for 15 sec). After a 20 min recovery period, the cultures were reexposed to AMPA (50 μm + 10 μm MK-801 for 15 sec), followed immediately by a 2 min pulse of the mitochondrial protonophore FCCP (750 nm + 10 μm MK-801). Fluorescent images were taken before AMPA exposure (A), at the peak [Ca2+]i rise seen during the initial AMPA exposure (B), and at the peak [Ca2+]i rise seen after the AMPA/FCCP exposure (C). After imaging, the cultures were fixed and stained for SMI-32 (D). Note that exposure to AMPA followed by FCCP (C) causes higher [Ca2+]i rises than occur with AMPA exposure alone (B). Thepseudocolorbar shows the Fura-2FF fluorescence ratio scale. Scale bar, 50 μm.