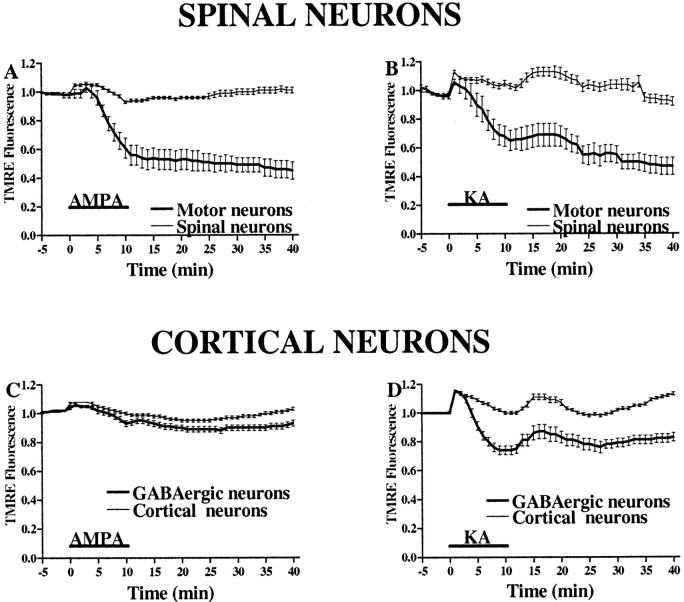
Fig. 7.
AMPA/kainate receptor activation causes greater mitochondrial depolarization in motor neurons than in GABAergic cortical neurons. In TMRE-loaded spinal (A, B) and cortical (C, D) cultures, the fluorescence in mitochondrial-rich regions was measured for 10 min before, during, and for 30 min after a 10 min exposure to AMPA (50 μm + 10 μm MK-801; A, C) or kainate (100 μm + 10 μm MK-801; B, D). Note the substantially greater decrease in fluorescence in motor neurons compared with GABAergic neurons after AMPA exposure in contrast to the similar fluorescence changes after kainate exposures.Traces represent the means ± SEM compiled from 10 to 17 motor and 150 other spinal neurons and from 40 to 70 GABAergic and 200 other cortical neurons from at least seven experiments.KA, Kainate.