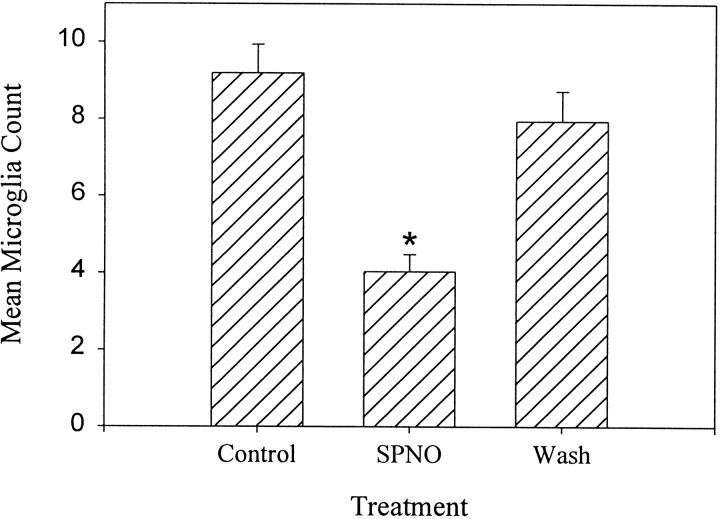
Fig. 5.
Quantitative comparison of the effect of SPNO on microglial accumulation. SPNO inhibited microglial cell accumulation, and this effect was reversible. Nerve cords were crushed and incubated in culture medium (Control) for 6 hr, 1 mm SPNO for 6 hr (SPNO), and 1 mm SPNO for 3 hr followed by a 3 hr wash in L-15 (Wash). Accumulation was measured by counting microglial cell nuclei that intersected a line at right angles to the long axis of the connectives (see Materials and Methods). The SPNO treatment significantly reduced microglial accumulation at the lesion site compared with controls. Washed cords (Wash) had cell counts similar to crush controls that sat for 6 hr in L-15 (Control) but were significantly different from cords that were incubated in 1 mm SPNO for 6 hr (SPNO) (ANOVA; Scheffe's test;F(2,6) = 20.87; p< 0.002; Newman–Keuls post hoc; p< 0.05; n = 5). Error bars are SEM. Groups significantly different from control are indicated by *.