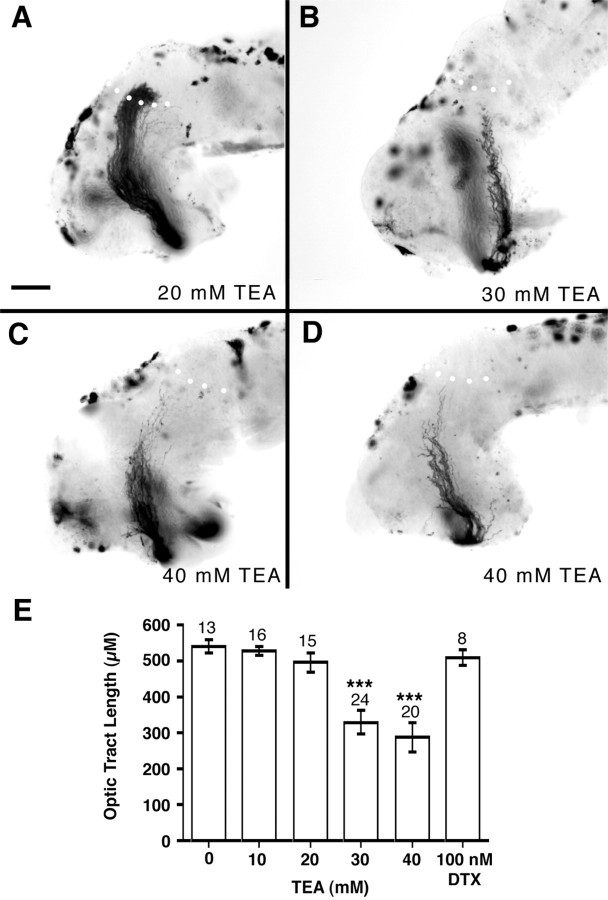
Fig. 9.
TEA treatment inhibits growing RGC axons.A–D, HRP-labeled optic projections in stage 40 whole-mount brains exposed at stage 33/34 to 20 mm(A), 30 mm (B), and 40 mm (C, D) TEA. Increasing concentrations of TEA result in shorter optic projections, but no obvious pathfinding or fasciculation errors. Scale bar (shown inA), 100 μm. E, Graph showing the mean optic tract length (converted to micrometers from BRUs) with increasing doses of TEA. Low concentrations of TEA (10–20 mm) had little or no effect on the optic projection, whereas the optic tract was significantly shorter in brains exposed to either 30 or 40 mm TEA (***p < 0.001). α-dendrotoxin at a concentration of 100 nm had no effect on the extension of optic axons (p > 0.5).Numbers above bars represent numbers of embryos.