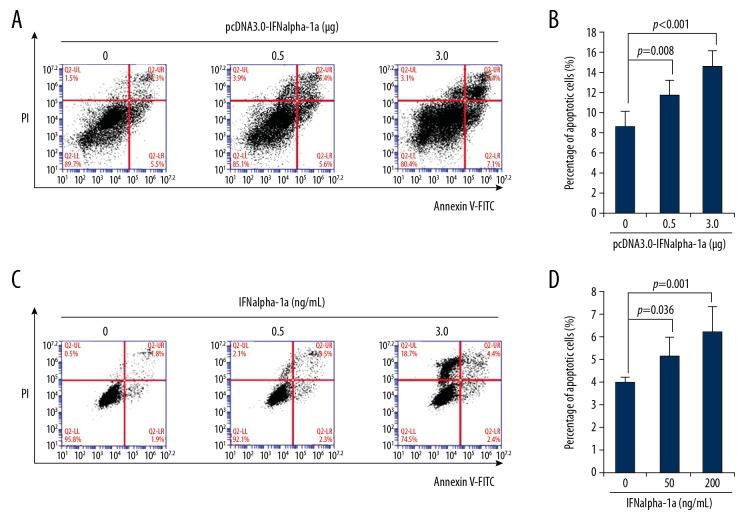
Figure 2.
IFNalpha-1a promotes the apoptosis of laryngeal carcinoma HEp-2 cells. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of the apoptosis of HEp-2 cells that were transiently transfected with pcDNA3.0-IFNalpha-1a. HEp-2 cells were first seeded onto a 12-well culture plate and transiently transfected with increasing doses (0, 0.5, and 3 ug) of pcDNA3.0-IFNalpha-1a. After 48-h incubation, the transfected HEp-2 cells were subjected to Annexin V/Propidium iodide (PI) double staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. (B) Quantitation of the apoptosis of the HEp-2 cells after transiently transfecting with pcDNA3.0-IFNalpha-1a. The transfected HEp2 cells in (A) were subjected to Annexin V/PI double staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. Each value is represented as mean ±SD from 3 independent experiments. After statistical analysis, results were considered to be significant if p≤0.05. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of the apoptosis of HEp-2 cells that were treated with recombinant human IFNalpha-1a. Hep-2 cells were seeded onto a 12-well culture plate and treated with increasing doses (0, 50, and 200 ng/mL) of recombinant human IFNalpha-1a. After 48-h culture, the cells were harvested and subjected to Annexin V/PI double staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. (D) Quantitation of the apoptosis of the HEp-2 cells after IFNalpha-1a treatment. The IFNalpha-1a treated HEp-2 cells were prepared as described in (C) and subjected to Annexin V/PI double staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. Each value is represented as mean ±SD from 3 independent experiments. After statistical analysis, results were considered to be significant if p≤0.05.