Figure 2.
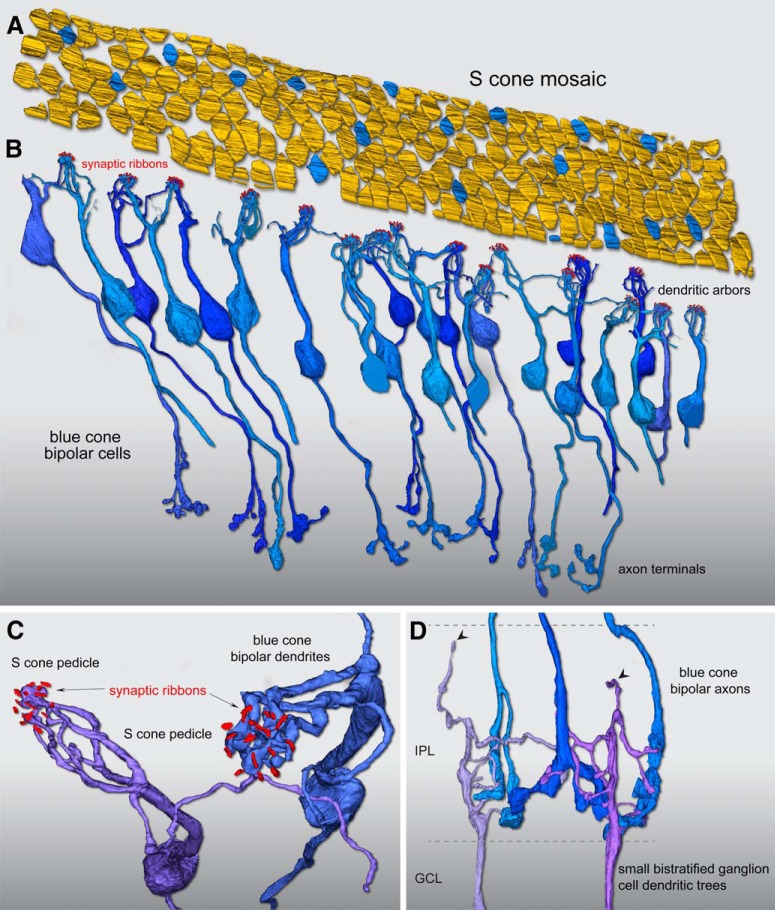
Reconstruction of foveal S-cone mosaic and blue cone (S ON) bipolar cell synaptic pathway. A, Outlines of the positions of 185 cone pedicle locations in the foveal volume (Fig. 1). Seventeen regularly spaced cones (9%) were identified as S cones (blue) by their small size and lack of telodendritic contacts with neighboring larger pedicles (Fig. 1). B, Confirming the S-cone identity of these 17 pedicles, each received all invaginating central element contacts from a single cone bipolar type with the morphology of the blue cone (S ON) bipolar as previously described, with branching dendrites that converge on and selectively contact only S-cone pedicles, and may contact one to three neighboring S cones. In this instance, we found 26 blue cone (S ON) bipolar cells in synaptic contact with these 17 S cones, occupying all central elements in the pedicle. C, Zoomed view looking vertically through the pedicle of two blue cone (S ON) bipolar cell dendritic processes forming invaginating terminals (Fig. 1C) at neighboring S-cone pedicles. For visibility, the pedicle volume was made transparent; synaptic ribbon volumes (red) are shown in relation to the bipolar dendritic arbors. D, The axons of the blue cone (S ON) bipolar cells branch and terminate at the inner border of the IPL (Fig. 1D), where they make synaptic contact with presumed blue ON small bistratified ganglion cells. Two ganglion-cell dendritic trees receive synaptic input from three blue cone (S ON) bipolar cell axon terminals at the inner border of the IPL. These two ganglion cells also show very sparse dendrites that extend to the outer half of the IPL (arrowheads), consistent with their identification as the blue ON small bistratified ganglion-cell type.