Figure 1.
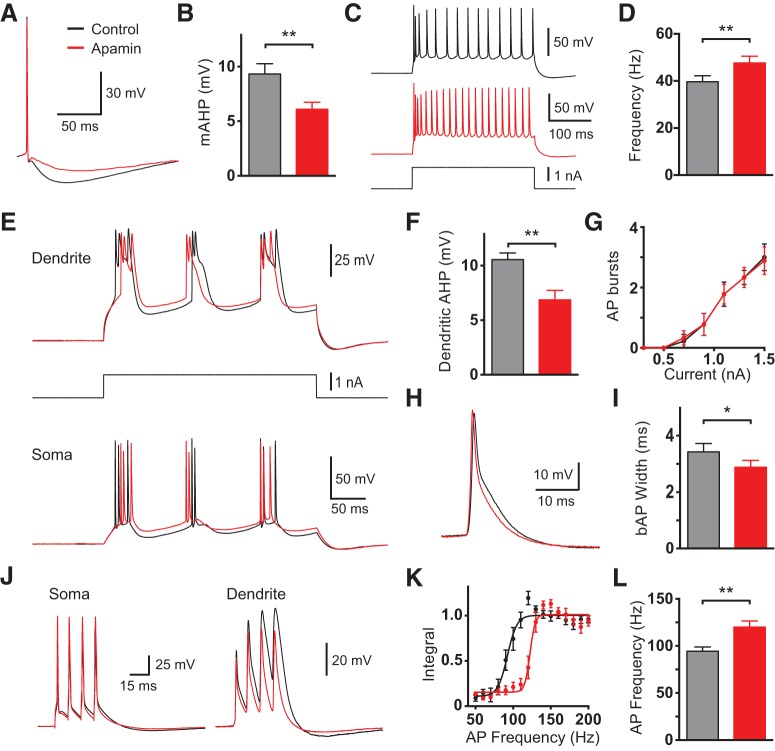
Effect of bath application of apamin on cell excitability. A, Somatic AP in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red). B, Average amplitude of the somatic mAHP in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; n = 10). C, Somatic response to a 500 ms current step (bottom) in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red). D, Average somatic firing frequency in response to 1.5 nA current steps in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; n = 10). E, Somatic (bottom) and dendritic (top; 700 μm from the soma) responses to a 300 ms dendritic current step (middle) in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; 100 nm). F, Average hyperpolarization after dendritic spikes (dendritic AHP) in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; n = 10). G, Average number of somatic AP bursts during dendritic current injections of different amplitude in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; n = 10). H, bAP in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; 700 μm from the soma). I, Average bAP width at 25% amplitude in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; n = 10). J, Somatic (left) and dendritic response (right; 600 μm from the soma) to four somatic APs at the critical frequency (100 Hz) in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red). K, Averaged, normalized dendritic voltage integral during AP trains at the indicated AP frequencies in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; lines represent sigmoidal fits; n = 10). L, Average critical frequency in control (black) and after bath application of apamin (red; n = 10).