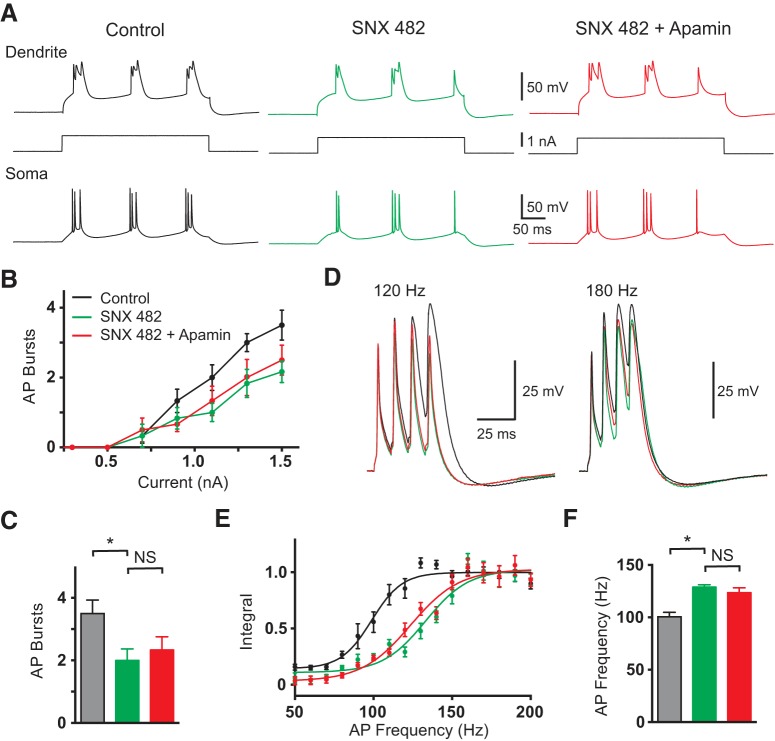
Figure 6.
Effect R-type calcium channels. A, Dendritic (top; 680 μm from the soma) and somatic (bottom) response to 300 ms dendritic current steps (middle) in control (black), after local dendritic SNX482 (green) and after local dendritic SNX482 plus apamin (red). B, Average number of AP bursts observed during dendritic current steps of varying intensity in control (black), after local dendritic SNX482 (green), and after local dendritic SNX482 plus apamin (red; n = 5). C, Average number of AP bursts during a dendritic current step of 1.5 nA in control (black), after local dendritic SNX482 (green), and after local dendritic SNX482 plus apamin (red; n = 5). D, Dendritic responses (630 μm from soma) to five somatic APs at 120 Hz (left) and 180 Hz (right) in control (black), after local dendritic SNX482 (green) and after local dendritic SNX482 plus apamin (red; n = 5). E, Averaged, normalized dendritic voltage integral during AP trains at the indicated frequencies in control (black), after local dendritic SNX482 (green) and after local dendritic SNX482 plus apamin (red; lines represent sigmoidal fits; n = 5). F, Average critical frequency in control (black), after local dendritic SNX482 (green) and after local dendritic SNX482 plus apamin (red n = 5).