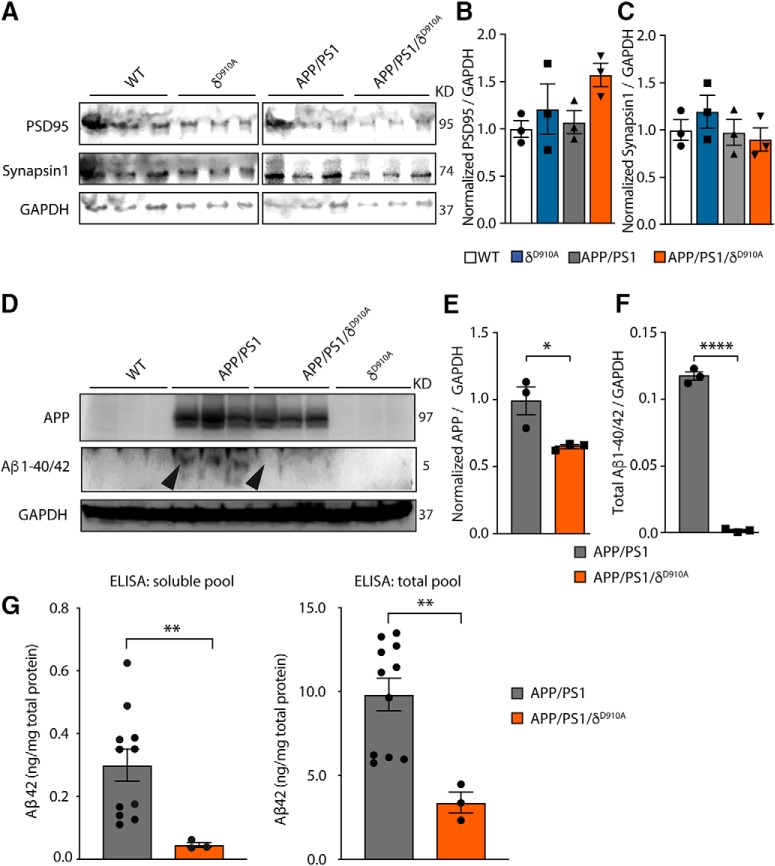
Figure 5.
Impact of genetic PI3Kδ inactivation on Aβ and APP levels in brains of APP/PS1 mice. A, Representative Western blot of PSD-95 and Synapsin-1 from brain extracts prepared from a different cohort of 12-month-old mice of indicated genotypes (3 animals per group). B, Densitometric measurements of PSD-95 normalized to GADP levels and to the average level obtained in WT mice. C, Densitometric measurements of Synapsin-1 normalized to GADP levels and to the average level obtained in WT mice. D, Representative Western blot of APP and Aβ1–40/42 from brain extracts prepared from the same 12-month-old cohort of mice. E, Densitometric measurements of APP normalized to GADP levels and to the average level obtained in APP/PS1 mice. F, Densitometric measurements of Aβ1–40/42 normalized to GADP levels. G, Quantification of the amount of total and soluble Aβ42 in cortical lysates of APP/PS1 and APP/PS1/δD910A mice by ELISA. The data of both genders of APP/PS1 were combined. No significant differences were found between males and females (p = 0.7922, data not shown). Data are displayed as mean ± SEM, n = 3 in B–D and F, n = 11 and 3 mice in G. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test comparing all groups with the WT group in B and C. Student's t test in E–G, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.