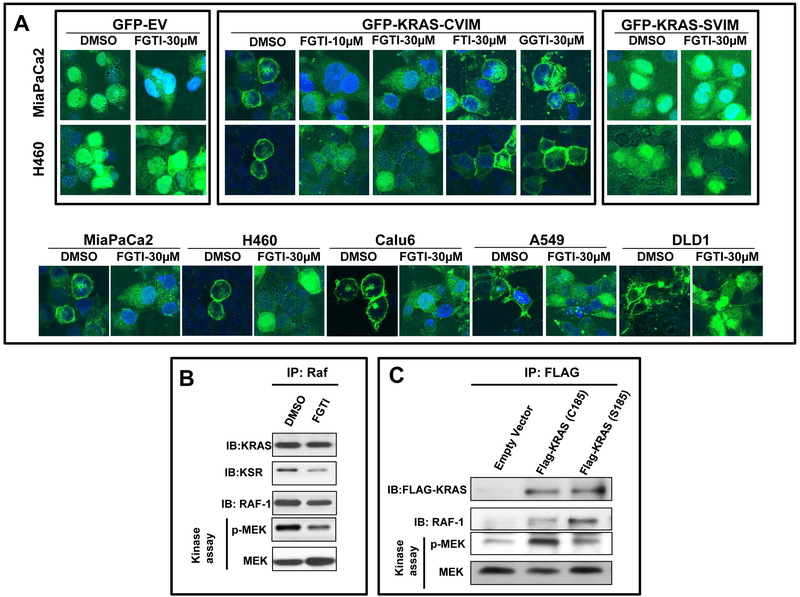
Figure 2. Effects of accumulating KRAS in the cytosol on binding to RAF-1 and KSR and on RAF-1 kinase activity.
A, FGTI-2734, but not FTI-2148 or GGTI-2418, inhibits membrane localization of GFP mutant KRAS-CVIM in human cancer cells. MiaPaCa2, H460, Calu6, A549, and DLD1 cells were grown on glass coverslips and infected with lentiviruses of GFP-tagged mutant KRAS-CVIM, GFP-tagged 185 Cys to Ser mutant KRAS that cannot be prenylated (GFP-mutant KRAS-SVIM), and corresponding empty vector (GFP-tagged-EV) and treated with vehicle control (DMSO) or FGTI-2734, FTI-2148, or GGTI-2418. Cells were fixed and viewed through a confocal microscope. B, FGTI-2734 inhibits RAF-1 kinase activity and binding to KSR but not to KRAS. MiaPaCa2 cells were treated with FGTI-2734 at 30 μM and processed for RAF-1 immunoprecipitation, followed by KRAS and KSR immunoblotting as well as RAF-1 kinase assay in the immunoprecipitates using recombinant inactive MEK1 as a substrate and western blotting with an antibody to phosphorylated Serines 217 and 221as described under Methods. C, The cytosolic CAAX mutant KRASG12V-SVIM binds RAF-1 but does not activate it. MiaPaCa2 cells expressing FLAG-tagged KRASG12V-CVIM or FLAG-tagged KRASG12V-SVIM were processed for coimmunoprecipitation and RAF-1 kinase assays as described above.