Fig. 4.
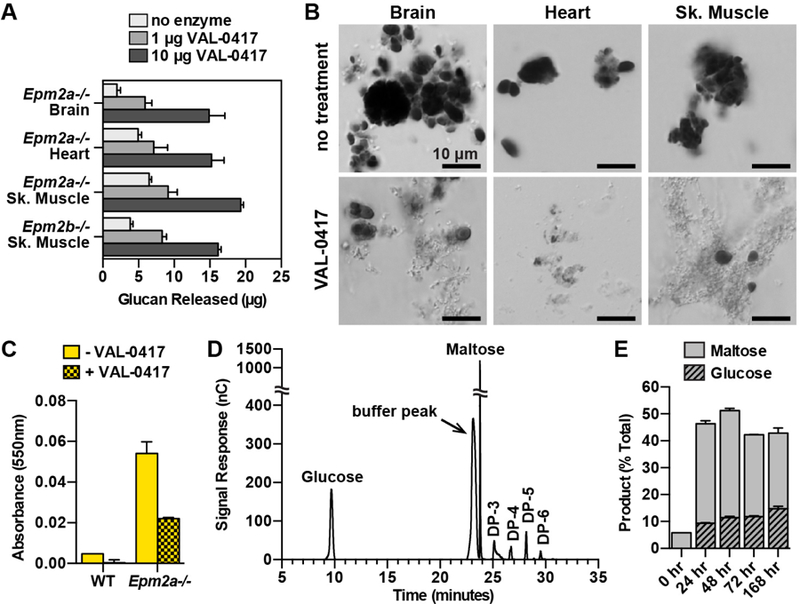
VAL-0417 degrades LBs in vitro. (A) Degradation of 50 µg LBs from different tissues after overnight incubation with 0, 1, or 10 µg VAL-0417. (B) LBs from different tissues after overnight incubation +/− 10 µg VAL-0417. Insoluble fractions were resuspended post-degradation, stained with Lugol’s solution, and visualized using a Nikon Eclipse E600. (C) Iodine absorbance in pellet fractions after incubation of WT and Epm2a−/− skeletal muscle homogenates +/− 25 µg VAL-0417. In (A), (C), and (E) mean ± SD of triplicates are shown. (D) HPAEC-PAD chromatogram of degradation product after incubation with VAL-0417 for 168 hours. Peak identities were determined based on the elution profile of degradation buffer and glucan standards. The chromatogram is representative of triplicate experiments, and glucose/maltose quantification from the replicates is shown in (E). (E) Quantification of glucose and maltose at various time points throughout the degradation reaction of LBs with VAL-0417. Product released are expressed as a percentage of total LBs. See also Figures S3 and S4.
