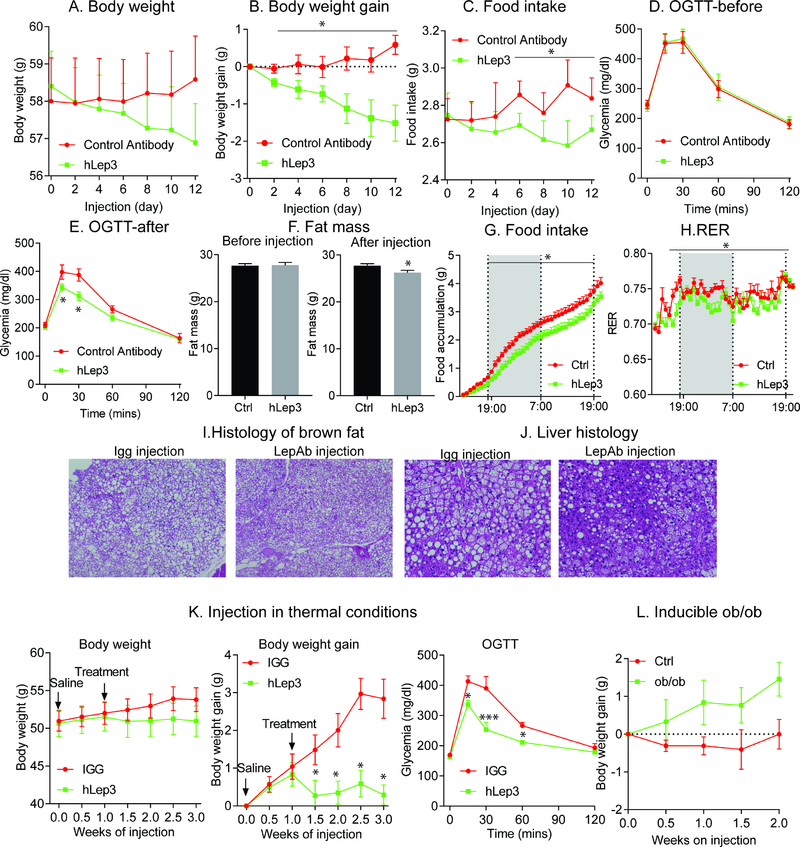
Figure 4. Decreasing leptin levels with neutralizing anti-leptin antibodies reduces body weight gain and liver steatosis.
A cohort of obese mice (n = 8 per group) were treated either with control antibody or leptin neutralizing antibody (hLep3) for two weeks. Antibody injections were done every other day. Body weight (A) and food intake (C) were measured before each injection. Body weight gain was calculated (B); OGTTs were performed before (D) and (E) after antibody injection; Total fat mass (F) was measured by Eco-MRI. For the metabolic cage studies, obese WT mice (n = 6 per group) were treated with a control antibody (hIGG) or hLep3 antibody. (G) Food consumption measured in metabolic cages after vehicle or hLep3 treatment; (H) RER measured in vehicle and hLep3 treated mice; After a two-week treatment period, mice were euthanized and brown fat and liver were collected for histology analysis. H&E staining of brown adipose tissue (I) and liver (J); Obese WT mice (n = 5 per group) were housed in thermoneutral chambers and treated with control antibody (hIGG) or hLep3 neutralizing antibody for two weeks (K) Effects of the neutralizing antibody hLep3 on body weight, body weight gain and OGTTs on mice housed at thermoneutrality; (L) Effect of hLep3 on body weight gain in inducible ob/ob mice.
(Data are given as mean ± SEM. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).