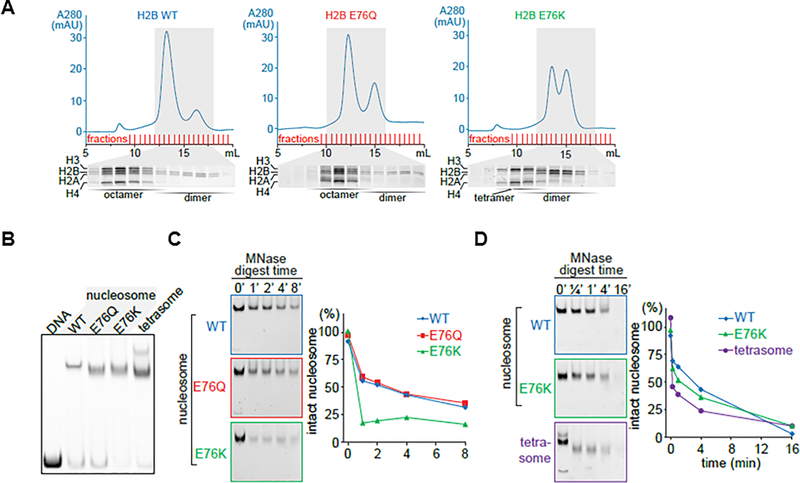
Figure 3: The E76K mutation in H2B destabilizes the histone octamer and fails to protect the nucleosome from nuclease treatment in vitro.
(A) The H2B-E76K mutant was unable to form stable octamers in vitro. Recombinant human histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) were mixed and histone octamers resolved from (H3/H4)2 tetramers, H2A/H2B dimers and free histones by gel filtration chromatography. (B) Nucleosomes were reconstituted by mixing equimolar amounts of DNA (147bp) and octamers or in the case of E76K of tetramers and dimers (1:2 molar ratio) and resolved by Native PAGE. Nucleosomes containing H2B-E76K and E76Q have an altered migration pattern, intermediate between a tetrasome and a WT nucleosome. (C) Micrococcal nuclease (MNase) sensitivity assay performed on nucleosomes made with WT, E76Q and E76K H2B mutants shows more rapid digestion of E76K containing nucleosomes than those with WT H2B. A time course by gel (left) and densitometry quantification (right) of intact nucleosomes following MNase treatment. (D) The MNase susceptibility of E76K nucleosomes is distinct from nucleosomes formed only with tetrasomes.